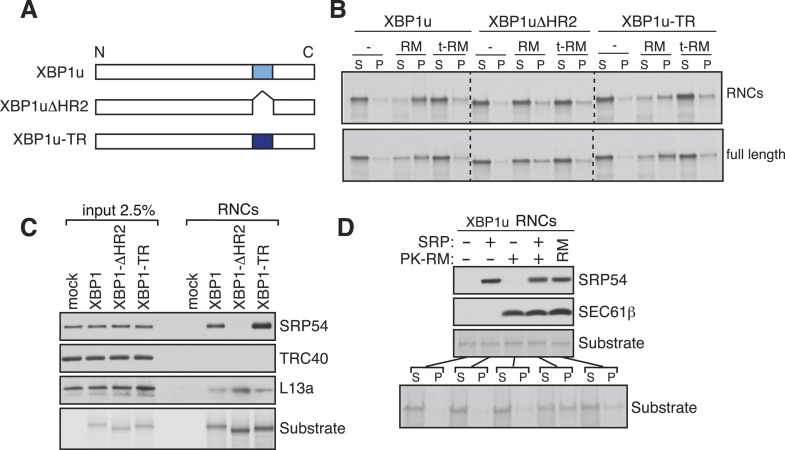
Figure 3. XBP1u utilizes the signal recognition particle (SRP) pathway for targeting its mRNA to the ER membrane.
(A) Diagram of constructs derived from XBP1u. Blue box denotes the previously described hydrophobic region 2 (HR2) of XBP1u (Yanagitani et al., 2009). Dark blue indicates the transmembrane domain (TMD) from the transferrin receptor in lieu of HR2. (B) The indicated versions of XBP1u transcripts lacking a termination codon were translated in rabbit reticulocyte lysate in the presence of rough microsomes (RM) or trypsin digested RM (tRM). The reactions were separated by centrifugation to analyze pellet (P) and soluble fractions (S) by SDS-PAGE and autoradiography. (C) Affinity purified ribosome associated nascent chains (RNCs) of the indicated versions of FLAG-tagged XBP1u were analyzed by IB for the indicated antigens. L13a is a ribosomal protein. TRC40 is a control protein. Autoradiography of the blot revealed equal recovery of translated substrates. (D) XBP1u transcripts lacking a termination codon were translated in the wheat germ translation system including purified SRP, puromycin/potassium acetate treated RM (PK-RM) or both. RM alone was included as a control. An aliquot of the total translation reaction was analyzed by IB for SRP54 and Sec61β, which indicate the presence of SRP and PK-RM, respectively. An autoradiograph of the blot revealed equal translation of substrate XBP1u in all reactions. The reactions were separated and analyzed as in panel B.