Figure 4.
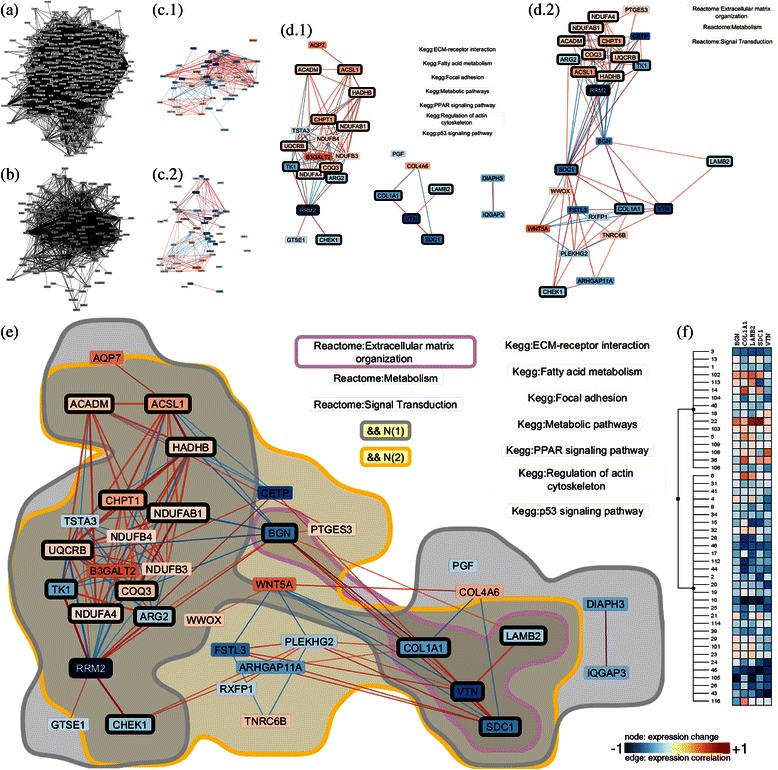
Integrating and comparing knowledge from multiple sources to explore novel findings in experimental data.(a) The complete data-knowledge network. (b) Filtered subnetwork after applying two continuous DoI functions. Again, the analyst used the statistical association of gene expression with LVEF response and the gene-expression correlation as DoI functions. Next, two discrete DoI functions are applied to extract subnetworks based on different knowledge sources (c.1) and (c.2). Individual subnetworks based on similar terms from KEGG (d.1) and Reactome (d.2) were created to analyze gene annotations individually. (e) Integrated data-knowledge network for comparison and analysis of the overlap. Genes contained in both subnetworks are highlighted by the black border (in (d.1), (d.2), and (e)) and both sets of genes—one set for each network—are surrounded by a contour. The analyst determined that the expression of multiple extracellular matrix proteins—highlighted and surrounded by a contour—according to both expert sources were correlated with LVEF response—confirmed using the heat-map view (f). In (c)-(e), the same color mapping is applied as in Figure 3.
