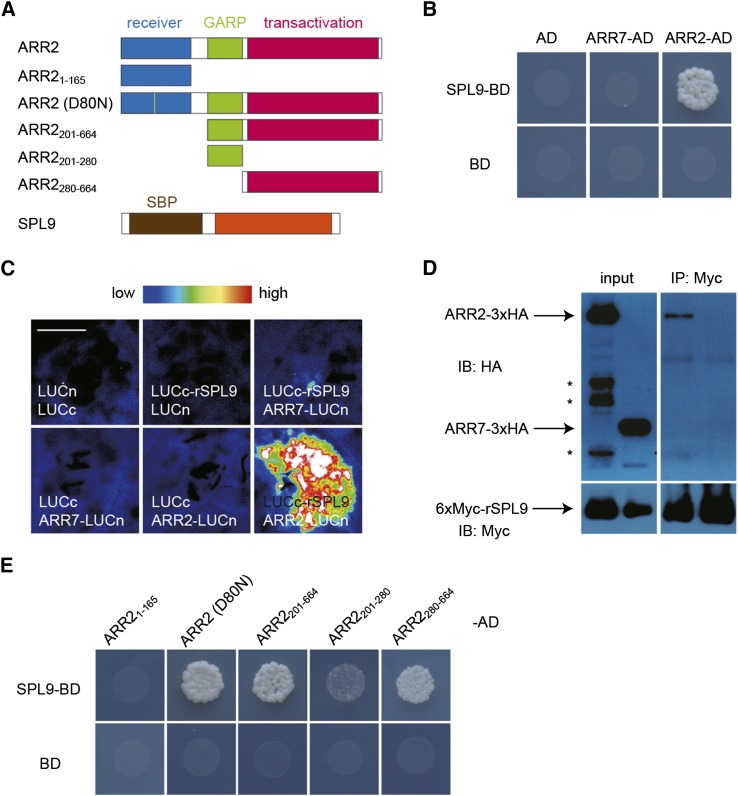
Figure 4.
miR156-Targeted SPL Binds to B-Type ARR.
(A) Diagrams of ARR2 and SPL9 constructs for interaction studies. The receiver, GARP, and transactivation domains of ARR2 are shown. The brown and orange boxes indicate the SBP domain and the C-terminal protein-protein interaction domain of SPL9, respectively.
(B) Yeast two-hybrid assay. ARR2 and ARR7 were fused to the GAL4 activation domain (AD) and SPL9 was fused to the GAL4 DNA binding domain (BD). Interaction assays were performed on an SD-Leu-Trp-His plate with 25 mM 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole.
(C) BiLC assay in N. benthamiana leaves. ARR2 or ARR7 was fused to the N-terminal domain of LUC (LUCn) and rSPL9 was fused to the C-terminal domain of LUC (LUCc). Bar = 0.5 cm.
(D) CoIP assay. ARR2-3xHA and 6xMyc-rSPL9 or ARR7-3xHA and 6xMyc-rSPL9 fusion proteins were transiently expressed in N. benthamiana leaves. Protein extract was immunoprecipitated (IP) with anti-Myc agarose beads and immunoblotted (IB) against anti-HA or anti-Myc antibody. Asterisks indicate degraded products of ARR2-3xHA.
(E) Yeast two-hybrid assay. The mutated or truncated form of ARR2 was fused to the GAL4-AD domain. Interaction assays were performed on an SD-Leu-Trp-His plate with 25 mM 3-amino-1,2,4-triazole.