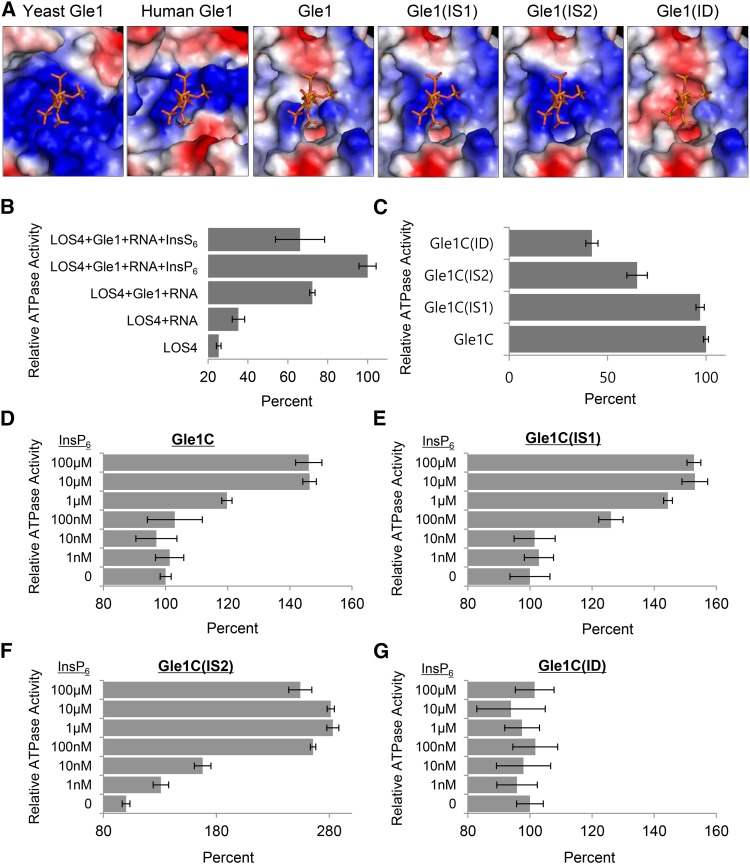
Figure 5.
InsP6 Sensitivity of Gle1 and Gle1 Variants for Stimulation of LOS4 ATPase Activity.
(A) InsP6 and InsP6 binding regions of human Gle1 and Arabidopsis Gle1 and its variants (IS1, IS2, and ID), which were predicted based on the structure of the yeast Gle1 domain. The electrostatic surface potential is shown: acidic, basic, and neutral residues are shown in red, blue, and white, respectively.
(B) Relative ATPase activity of LOS4 with different combinations of cofactors. ATPase assays were performed with 1 μM LOS4-His and 2 mM ATP in the presence or absence of the following cofactors: 2 μM MBP-Gle1 (full-length), 50 μg/μL polyadenylic acid (RNA), 10 μM InsP6, and 10 μM InsS6. Values in (B) to (G) represent means ± sd of three replicates per experiment.
(C) Stimulation of LOS4 ATPase activity by Gle1 and Gle1 variants in the absence of InsP6. ATPase assays were performed with 1 μM LOS4-His, 2 mM ATP, and 50 μg/μL RNA in the presence of MBP-Gle1C or MBP-Gle1C variants at a concentration of 2 μM.
(D) to (G) InsP6 sensitivity of Gle1 and Gle1 variants for LOS4 stimulation. ATPase assays were performed as described in (C) but in the presence of different InsP6 concentrations.