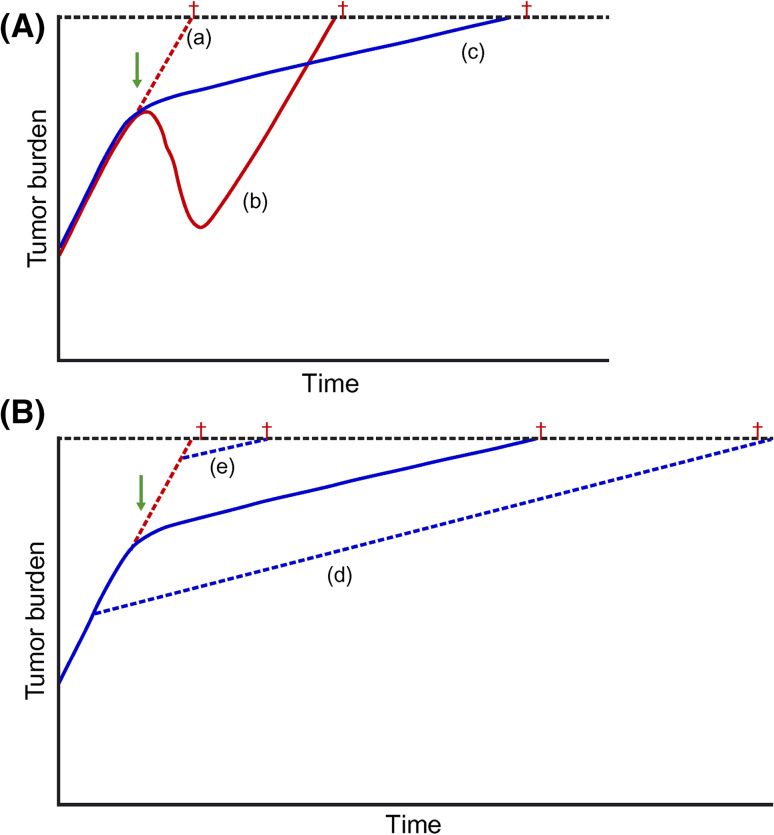
Fig. 4.
Proposed kinetics of immunomodulatory treatments. In a, immunotherapy is compared with cytotoxic chemotherapy. Tumor burden is shown if a no therapy is initiated, b chemotherapy is initiated, or c immunomodulatory therapy is initiated. For patients who received immunotherapy, there may be little if any reduction in tumor size, and therefore little or no increase in time to progression, but an increase in OS. Dagger denotes time of death. In b, early versus late initiation of immunomodulatory therapy is explored. The survival benefit may be increased if immunomodulatory treatment is initiated earlier in disease progression (d) but may be decreased in patients with a large tumor burden (e). Reproduced from Schlom J. Therapeutic cancer vaccines: current status and moving forward. J Natl Cancer Inst 2012;104(8):599–613, by permission of Oxford University Press [31]. OS overall survival