Fig. 5.
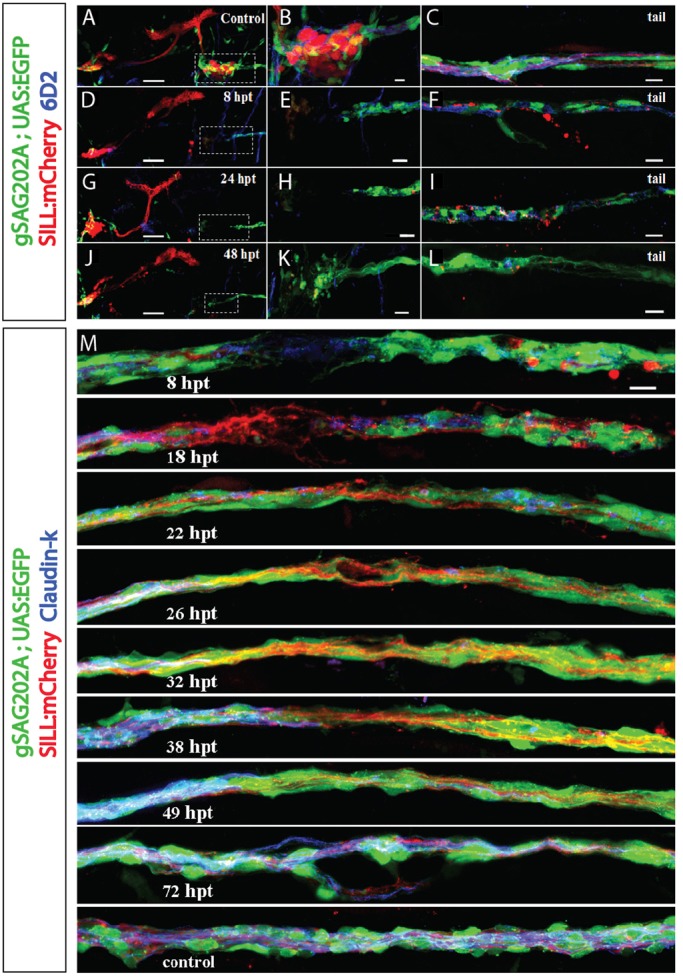
Gradual loss of expression of myelin glycoprotein and Claudin-k junctional protein upon axon severing or ganglion ablation. (A-L) Maximal projection of Tg[gSAGFF202A;UAS:EGFP;SILL:mCherry] larvae immunolabeled with myelin 6D2 antibody (blue). (A,D,G,J) The cephalic region showing the anterior and posterior ganglion before ganglionostomy (A) and at 8-48 hpt in fish with ganglion ablation (D,G,J). (B,E,H,K) Higher magnification of the boxed regions in A,D,G,J, respectively. (C,F,I,L) Images of the animals’ tail, corresponding to A,D,G,J. (D,G,J) At 8 hpt, 24 hpt, 48 hpt, immunostaining images reveals gradual loss of myelin protein. (F,I,L) Immunostaining of fish tails delineates the loss of myelin and clearance of axon debris in a gradual manner. (M) Time-course analysis of axonal regeneration and Claudin-k junctional protein expression (blue) in the Schwann cells around the site of damage. Claudin-k is present along the perineurium in control fish (lowest panel). A marked reduction of Claudin-k in the perineurium distal to the cutting site can be seen at 8 hpt. Distal Claudin-k protein levels remain lower than on the proximal part of the perineurium even after axonal regeneration at 26 hpt, and only level-up around 72 hpt. Scale bars: 50 μm (A,D,G,J), 10 μm (all others).
