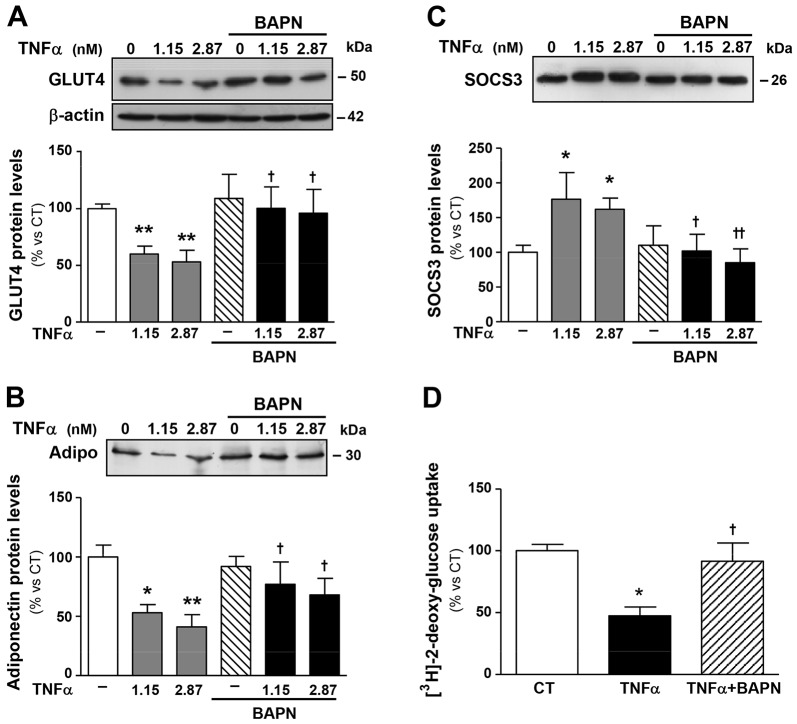
Fig. 5.
LOX inhibition influences glucose uptake and the expression of factors involved in the control of insulin sensitivity in an in vitro model of insulin resistance. Protein levels of (A) glucose transporter type 4 (GLUT4), (B) adiponectin (Adipo) and (C) suppressor of cytokine signaling 3 (SOCS3). 3T3-L1 adipocytes were stimulated with or without TNFα (1.15 and 2.87 nM, equivalent to 20 and 50 ng/ml, respectively) for 72 h in the presence of either vehicle or β-aminopropionitrile, an inhibitor of LOX activity (BAPN, 200 µM). Data that were normalised to the expression of β-actin are expressed as mean±s.d. of four assays in arbitrary units. (D) Insulin-stimulated glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Bars on graphs represent the mean±s.d. of the counts of [3H]-2-deoxyglucose normalised to the amount of total protein. Values are mean±s.d. of four assays. *P<0.05, **P<0.01 vs unstimulated cells (TNFα=0); †P<0.05, ††P<0.01 vs cells stimulated with the same concentration of TNFα in the absence of BAPN.