Fig. 3.
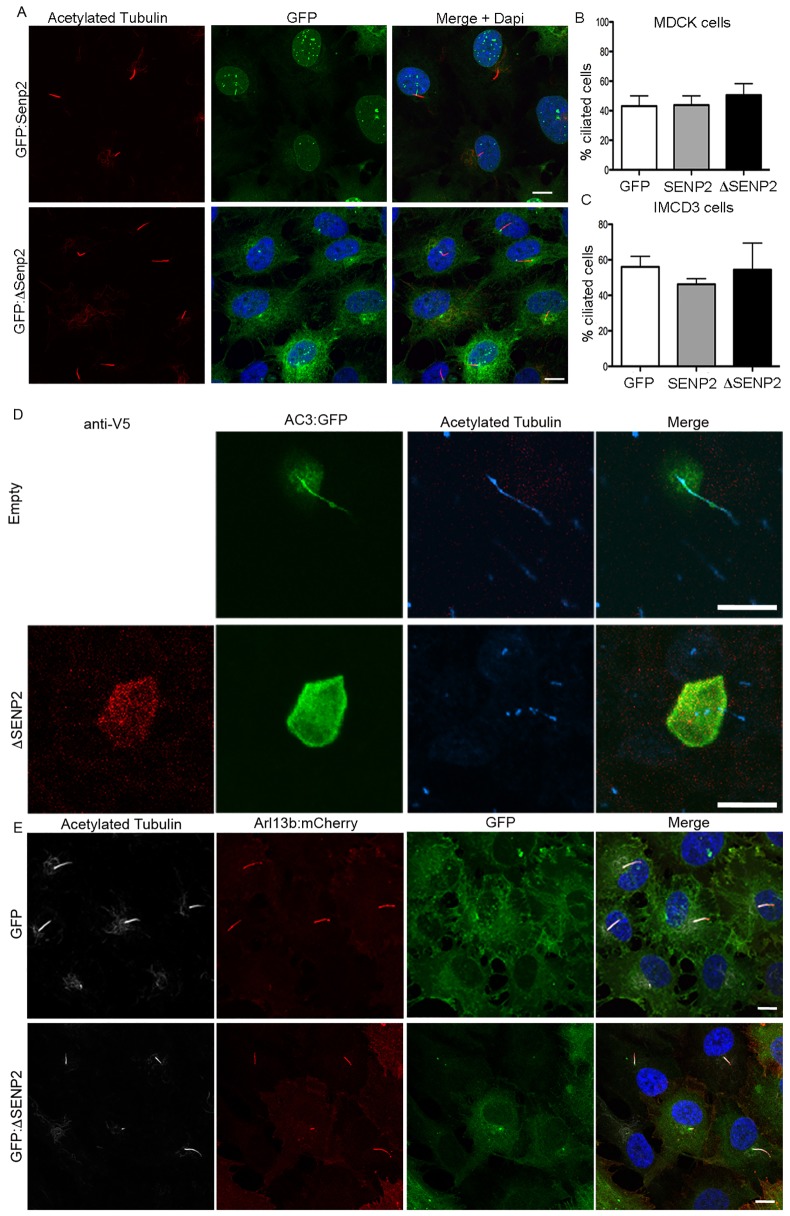
Overexpression of ΔSENP2 blocks ciliary localization. (A) Transduction of IMCD3 cells with GFP–SENP2 (GFP:SENP2, top) reveals SENP2 localization to the nuclear membrane, whereas expression of a N-terminus truncation (amino acids 1–82) of SENP2 (GFP:ΔSENP2; bottom) results in accumulation at the base of cilia. Neither SENP2 nor ΔSENP2 alters the presence of cilia as seen by immunostaining for acetylated α-tubulin in IMCD3 cells. (B,C) Quantification of the percentage of ciliated cells following transfection with either GFP, GFP–SENP2, or GFP–ΔSENP2 in both IMCD3 (B) or MDCKII (C) cells. Results are mean±s.e.m. (n=3 replicates per treatment). (D) AC3–GFP (AC3:GFP) localizes to cilia of MDCK cells as seen by colocalization with acetylated α-tubulin. Co-expression of AC3–GFP with ΔSENP2 prevents AC3–GFP localization in cilia. (E) Co-expression of GFP–ΔSENP2 with Arl13b–mCherry does not alter its entry to the cilium as seen by colocalization with acetylated tubulin. Scale bars: 10 μm.