Figure 1.
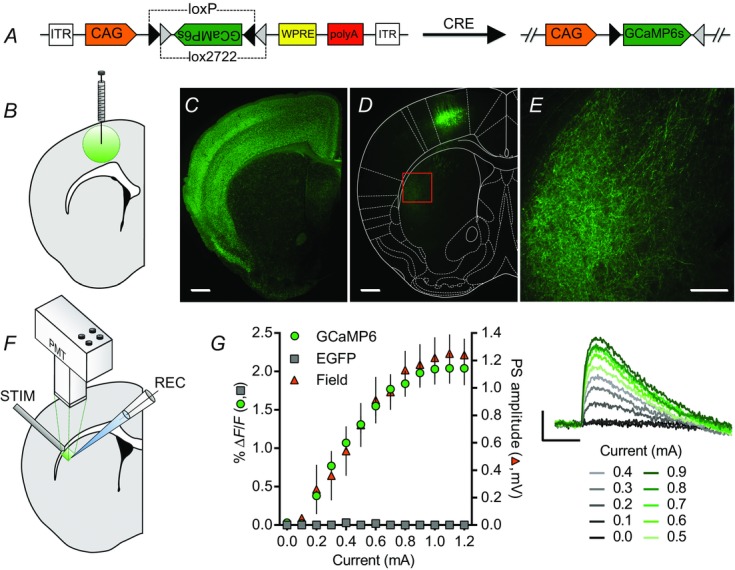
GCaMP6s expression in corticostriatal inputs to dorsolateral striatum
A, schematic diagram of the AAV-FLEX-GCaMP6s construct. In the presence of Cre recombinase, permanent recombination of two pairs of loxP and lox2272 sites changes the orientation of the GCaMP6 sequence from anti-sense to sense with respect to its promoter, CAG. B, schematic diagram of an AAV-FLEX-GCaMP6s injection into M1. C, cre-mediated expression of EGFP preferentially in cortical pyramidal neurons (and cortical glia; Gorski et al. 2002) in a striatal-containing coronal brain slice from an Emx1Cre;CAG-floxedSTOP-ZsGreen mouse. D and E, cre-mediated GCaMP6s expression in M1 cortical pyramidal cells (D) and presynaptic corticostriatal elements in the DLS (D, E) of an Emx1Cre mouse injected with AAV-FLEX-GCaMP6s into M1. The area shown in E is indicated by the box in D. F, schematic diagram of brain slice photometry and electrophysiology recordings. A concentric bipolar stimulating electrode placed at the border of the DLS and overlying white matter evoked striatal fluorescent transients detected by a photomultiplier tube (PMT) and striatal field potentials detected by a glass recording electrode. G, current–response curves of 100 μs electrical pulse-evoked fluorescence and field potentials recorded in the DLS of Emx1Cre mice injected with AAV-FLEX-GCaMP6s or AAV-FLEX-EGFP. GCaMP6s- (green circles, n = 6) but not EGFP-injected mice (grey squares, n = 6) showed evoked fluorescent transients that scaled with stimulation current amplitude and population spike (PS) amplitude (orange triangles, n = 6) (traces on right; average of four evoked responses per current amplitude). Scale bars of fluorescence images: 500 μm (C, D), 200 μm (E). Scale bars of evoked PreCaTs from AAV-FLEX-GCaMP6s-injected Emx1Cre mice: 1% ΔF/F, 0.5 s (G).
