Figure 5.
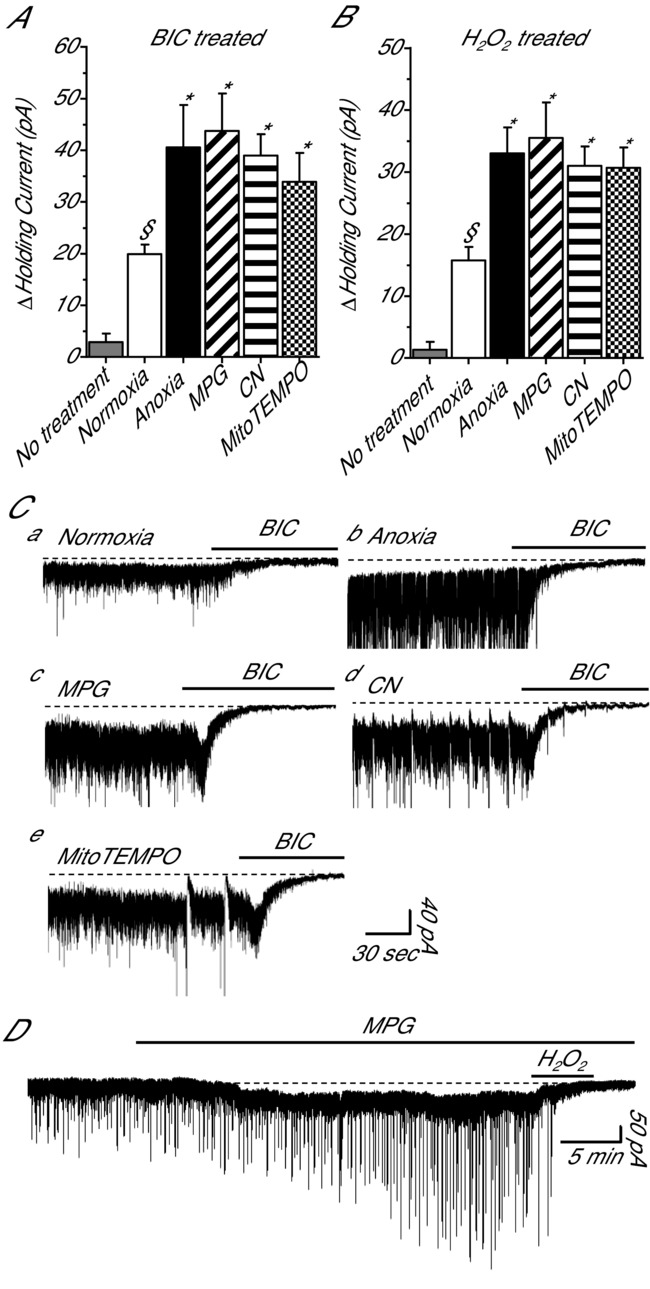
Tonic GABAA receptor currents in cortical pyramidal neurons are inhibited by H2O2 A, summary of the effects of bicuculline on tonic GABAA receptor currents following normoxia, anoxia, MPG or CN. B, summary of the effects of H2O2 on tonic GABAA receptor currents following the same treatments as in A. Note: no treatment (grey bars) in A and B represent the average change in the holding current prior to application of BIC or H2O2, respectively. C, sample raw traces used to generate A. D, sample raw trace used to generate B. Bars denote treatment duration. Dashed lines highlight the GABA-mediated tonic current. Pyramidal neurons were voltage clamped at −100 mV and GABAA receptor currents were enhanced with high [Cl−] pipette solution (130 mm) and isolated with NMDA and AMPA receptor antagonists (AP5 and CNQX, respectively; 25 μm each). Treatments: normoxia (95% O2/5% CO2-bubbled aCSF), anoxia (95% N2/5% CO2-bubbled aCSF), MPG (0.5 mm), CN (0.5 mm), BIC (100 μm) and H2O2 (50 μm). Data are means ± SEM, n = 5–7 replicates per treatment. §Significant difference from baseline. *Significant difference from normoxic controls (P < 0.05).
