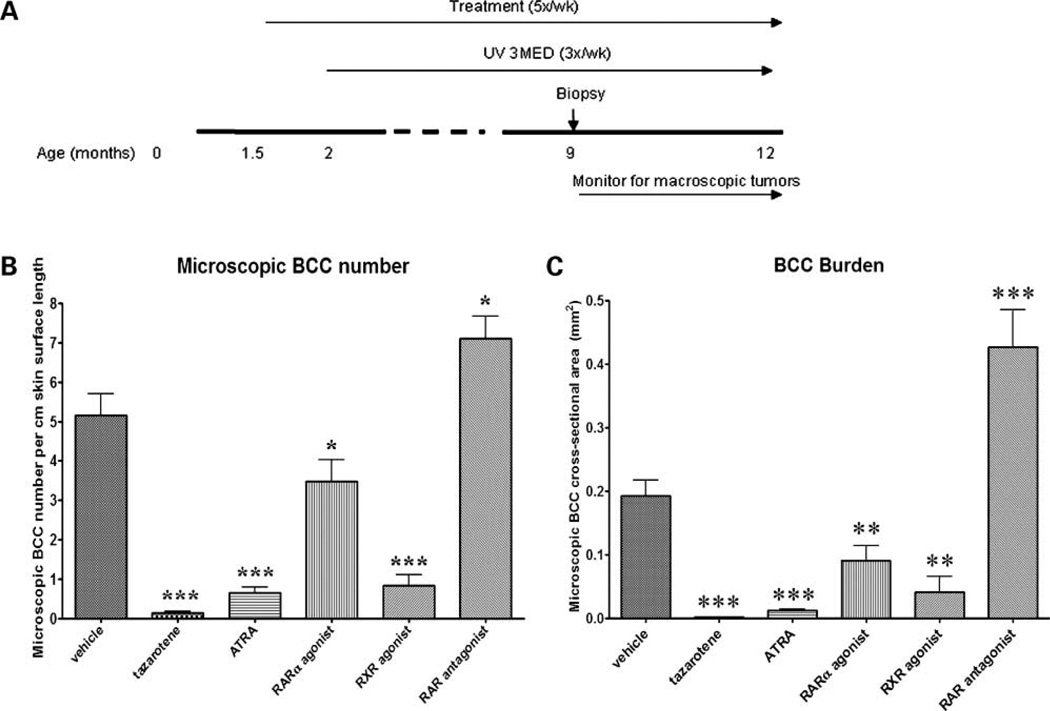
Figure 5.
Effects of retinoid-related agents on microscopic BCC tumorigenesis. A, timeline of retinoid chemoprevention study. B, mice were topically treated with retinoid agonists, vehicle, or a RAR antagonist from age 1.5 months and from age 2 months, exposed to UV continuously until age 12 months. Biopsies taken at age 9 months indicated that mice treated with tazarotene had the lowest number of microscopic BCCs (n = 31) followed by those mice treated with ATRA (n = 33) or the RXR agonist (n = 11). Mice treated with the RARα agonist (n = 20) had slightly fewer BCC lesions than the vehicle control mice (n = 26), whereas mice treated with the RAR antagonist appeared to have a slight increase in microscopic BCC number (n = 22); compared with vehicle-treated mice. C, topical treatment with tazarotene, ATRA, RARα, and the pan-RXR agonist significantly reduced the microscopic BCC tumor burden compared with vehicle treatment. RAR antagonist-treated mice developed more microscopic BCC lesions than vehicle-treated mice. Note: One microscopic BCC lesion that arose in the pan-RXR agonist-treated mice was an “extreme” outlier (0.13 mm2) and was not included in the graphical and statistical analyses because this lesion size appeared to be an anomaly. *, P < 0.05; **, P < 0.01; ***, P < 0.0001.