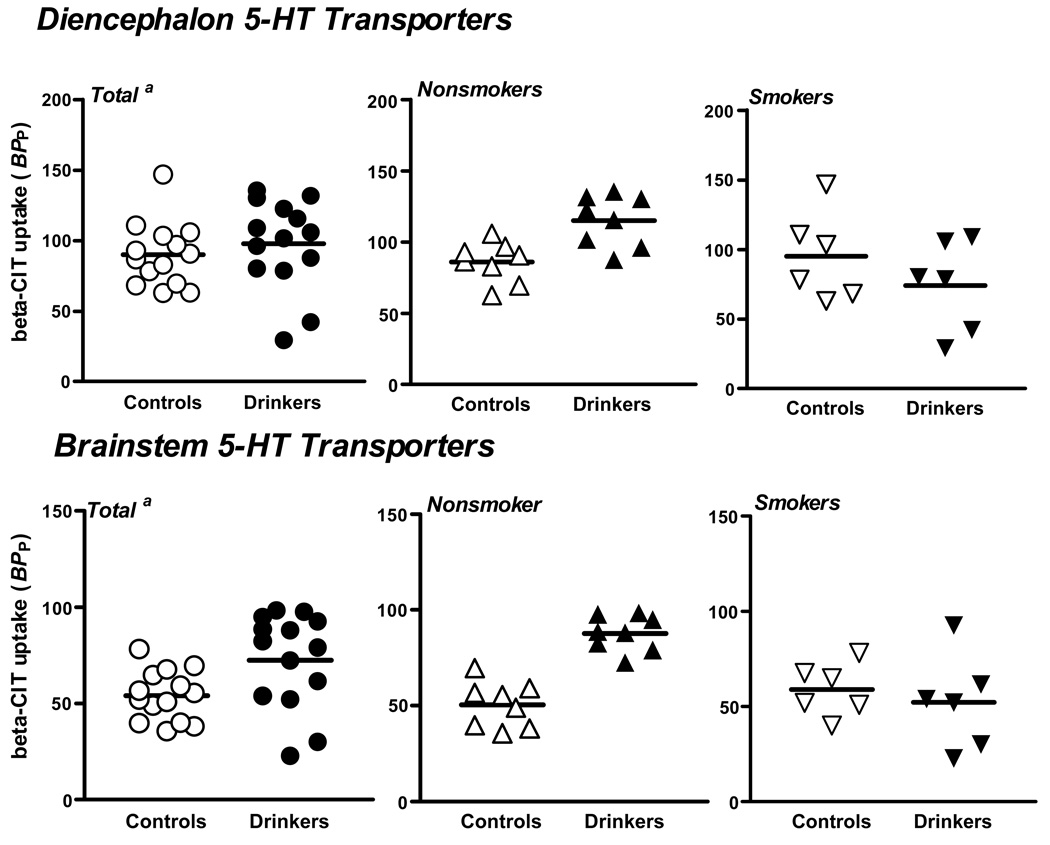
Figure 2.
Diencephalon and brainstem [123I]β-CIT binding in controls and alcohol drinkers in the total group and by smoking status. a. In the total group, there was an 8% difference (P=0.01), in the nonsmokers a 26% difference (P=0.04), and in the smokers a −28% difference (P=0.30). b. In the total group, there was a 25% difference (P=0.001), in the nonsmokers a 42% difference (P<0.0002), and in the smokers a −13% difference (P=0.90).