Fig. 4.
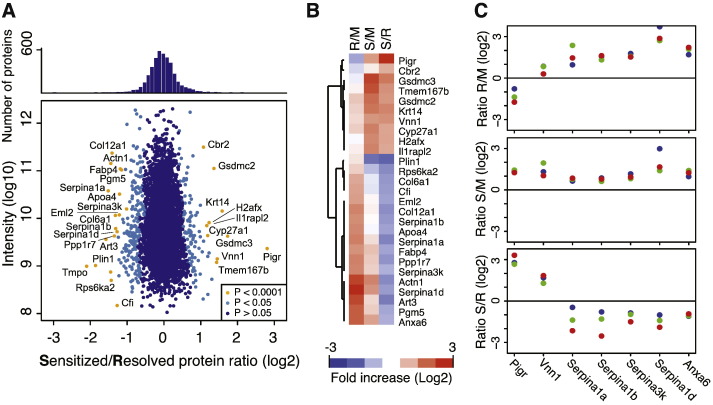
Proteomics identifies urothelial remodeling changes in sensitized mice that would render the bladder more susceptible to severe inflammation and neutrophil-mediated damage. (A) Quantitative proteomics analysis of convalescent bladder epithelia identified 4008 proteins. Average protein ratios for sensitized (S) versus resolved (R) bladders show the strongest enrichment or depletion for 27 proteins. (B) Heat map and tree of proteins with P value ≤ 0.0001 in the S/R comparison, also showing differences relative to age-matched mock (M) infected mice. (C) Data from a subset of proteins that are involved in inflammatory responses, showing the individual data points from each mouse in the three pairwise comparisons. See also Table S2.
Proteomics identifies urothelial remodeling changes in sensitized mice that would render the bladder more susceptible to severe inflammation and neutrophil-mediated damage. (A) Quantitative proteomics analysis of convalescent bladder epithelia identified 4008 proteins. Average protein ratios for sensitized (S) versus resolved (R) bladders show the strongest enrichment or depletion for 27 proteins. (B) Heat map and tree of proteins with P value ≤ 0.0001 in the S/R comparison, also showing differences relative to age-matched mock (M) infected mice. (C) Data from a subset of proteins that are involved in inflammatory responses, showing the individual data points from each mouse in the three pairwise comparisons. See also Table S2.