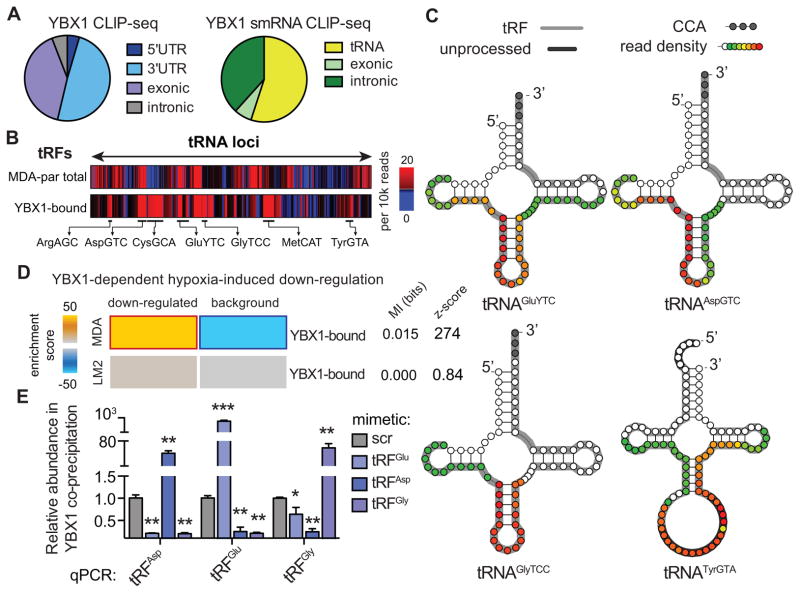
Figure 2. Endogenous YBX1 interacts with a large regulon of transcripts and small-RNAs in vivo.
(A) Pie-charts depicting the annotation of YBX1 binding sites obtained from immunoprecipitation of endogenous YBX1 from RNase-treated lysate of UV-irradiated MDA-parental cells followed by high-throughput sequencing of both long- and small-RNAs. (B) Relative frequency of reads mapped to each tRNA-locus in MDA-parental small-RNA sequencing and YBX1 small-RNA CLIP-seq. The tRF species most abundantly bound by YBX1 are marked. (C) Based on the YBX1 small-RNA CLIP-seq results, four species of tRNA-derived RNA fragments (tRFs) bound by YBX1 in vivo were identified. Shown are examples of tRNA structures for each species depicting the boundaries of the identified tRFs along with the YBX1 binding region based on smRNA YBX1 CLIP-seq read density at each position (also see Figure S2A). The grey nucleotides at the 3′ end mark the presence of terminal CCA sequences. The dark grey highlights for tRNATyrGTA mark the leader and intronic sequences in the unprocessed tRNA. The longest identified form of each tRF based on our high-throughput sequencing results are also indicated (grey highlight) along with the YBX1 smRNA CLIP-seq read density at each position (overlaid as a heatmap) indicating the YBX1 binding site. (D) Gene-expression profiling of control and YBX1-knockdown cells was performed under normal and hypoxic conditions in both MDA-parental and MDA-LM2 backgrounds. The set of transcripts that was down-regulated under hypoxia in a YBX1-dependent manner was identified for each cell-line. While YBX1-bound transcripts were significantly enriched among YBX1-dependent hypoxia-induced downregulated transcripts in MDA-parental cells, this enrichment was absent in the highly metastatic MDA-LM2 cells. (E) qPCR-based validation of interactions between YBX1 and tRFAspGTC, tRFGluYTC, and tRFGlyTCC. Cells transfected with exogenous tRF mimetics were subjected to UV-crosslinking and YBX1 immunoprecipitation. The abundance of each tRF in the co-immunoprecipitated RNA population was then measured using a small-RNA qPCR-based quantitation assay (n=3–4). Statistical significance is measured using one-tailed Student’s t-test: *, p<0.05, **, p<0.01, and ***, p<0.001. Error bars in all panels indicate s.e.m. unless otherwise specified.