Figure 1.
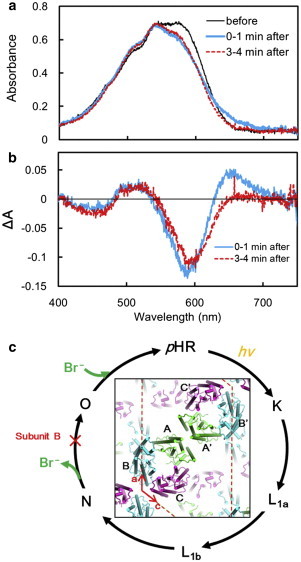
Light-induced absorption changes in the C2 crystal at 240 K. (a) The C2 crystal was cooled to 240 K under a flow of cold nitrogen gas and its absorption spectrum was recorded before illumination (black line), 0–1 min (blue line), and 3–4 min (red line) after illumination with orange light (>540 nm, ∼100 mW/cm2). For this measurement, a crystal adhered to a lower glass in the sitting-drop crystallization kit was soaked in a postcrystallization solution consisting of 0.01 M NaBr, 3.0 M ammonium sulfate, 0.1 M HEPES at pH7, and 30% trehalose, and mounted on an x-y stage attached to an optical microscope; the crystal orientation was then adjusted so that the b axis was parallel to the optical path of the measuring light beam. (b) Difference absorption spectra derived by subtracting the absorption spectrum of the unilluminated crystal from the spectra recorded after illumination. (c) The anion-transporting photocycle of pHR. (Inset) Protein packing in the C2 crystal, viewed along the b axis. To see this figure in color, go online.
