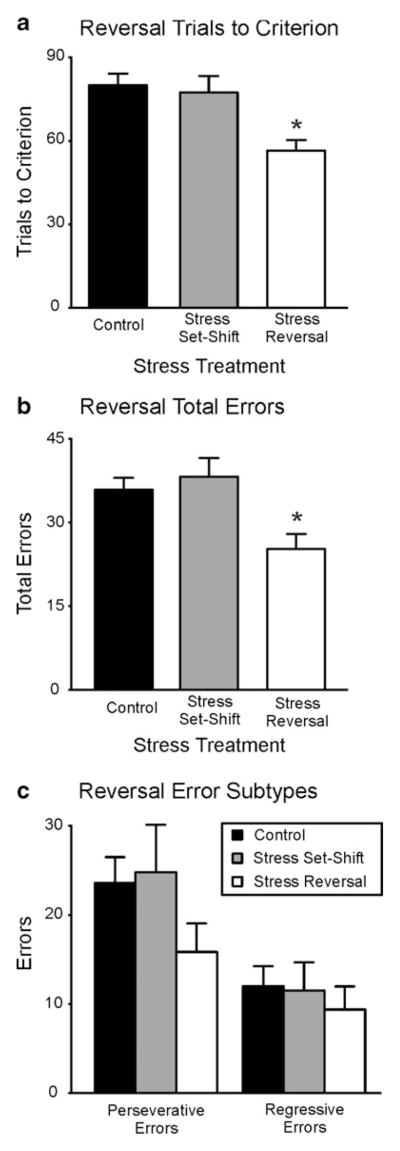
Fig. 3.
Effect of acute stress on reversal learning. a Trials to criterion. b Total errors. c Error subtypes. The rats acutely stressed prior to reversal learning reached criterion significantly faster and with fewer total errors than did rats from the other two groups. However, the numbers of perseverative and regressive errors committed were not significantly different between the groups. No stress, n = 16; stress before set-shifting, n = 10; stress before reversal learning, n = 13. *p < .05