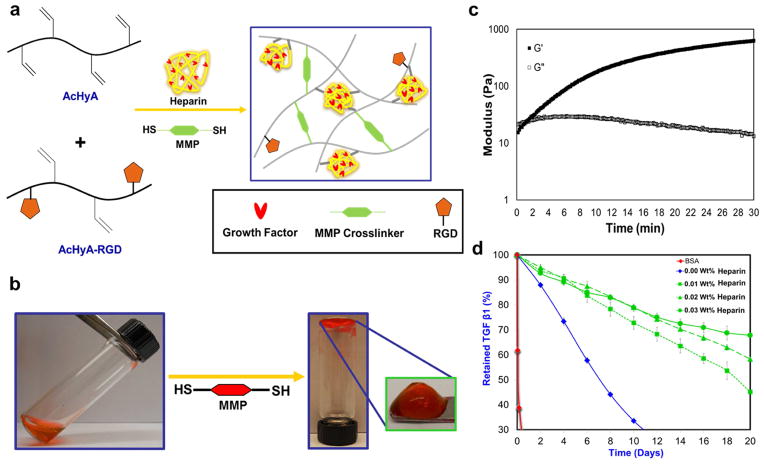
Figure 1. Schematic for gel synthesis.
a, HyA hydrogels containing the cell adhesive bspRGD(15) peptide and heparin as a growth factor presenting agent were synthesized by using bis-cysteine matrix metalloproteinase (MMP)-degradable peptide crosslinkers that reacted via the Michael-type addition to acryl groups on the functionalized HyA precursors. b, Images of polymerized hydrogel – red dye is for fiduciary purposes. c, The time required to initiate gelation, defined when the storage modulus (G′) exceeds the loss modulus (G″) occurred within 60 seconds. Gelation was considered complete when G′ reached a plateau, and occurred within 15 minutes, depending on the weight ratio of HyA included in each hydrogel. d, Depending on the weight percentage of heparin present, HyA hydrogels (0.03 wt.% heparin) retain over 70% of the TGFβ1 for up to 20 days. Hydrogel with a lower wt% of heparin (e.g. 0.01wt.%) exhibitted a slow and nearly zero order release kinetics. Gels without heparin released most of the TGFβ1 by 10 days. There was minimum retention of BSA within the HyA hydrogels, which has acidic isoelectric point, confirming that molecular diffusion was not hindered by the crosslinking density of hydrogel.