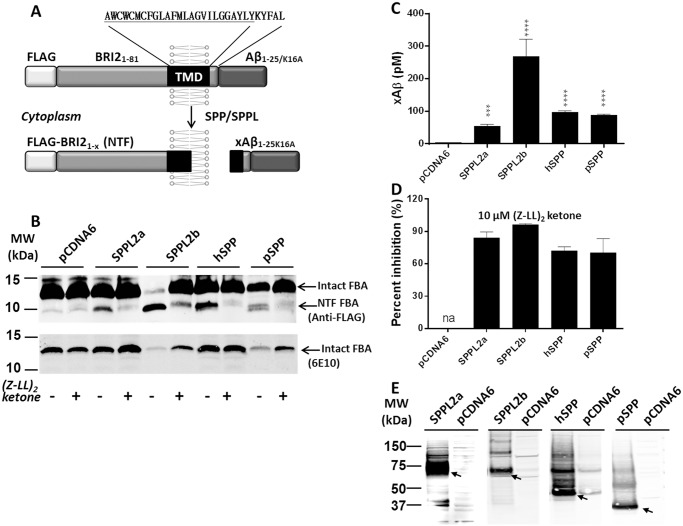
Fig 1. The FBA substrate is efficiently cleaved by SPP/SPPLs.
A. Design of SPP assay substrate based on BRI2 transmembrane domain. A FLAG tag fused to the NH2-terminus of BRI21-81. Aβ1-25/K16A fused to the COOH-terminus of BRI21-81. Potential cleavage in the transmembrane domain releases the ectodomain fragment xAβ1-25/K16A. B. Western blotting of FBA ±SPPL transfected cell lysates with and without 10 μM (Z-LL)2 ketone. Blot detected with anti-FLAG M2 antibody. The intact FBA and ICDs are marked with arrows. C. SPP/SPPLs significantly increase xAβ1-25/K16A secretion from FBA transfected cells. xAβ1-25/K16A levels were determined with Aβ ELISA. D. The FBA cleavages conducted by SPPLs co-transfection are largely inhibited by 10 μM (Z-LL)2 ketone. E. Western blotting of SPPLs transiently transfected HEK cell lysates. Blots detected with antisera against SPPL2a, SPPL2b, hSPP, and pSPP respectively. Monomer bands are marked with arrows. All experiments repeated 3 times. Statistical analysis performed by 1-way ANOVA ((*p<0.05, **p<0.01, ***p<0.001, ****p<0.0001).