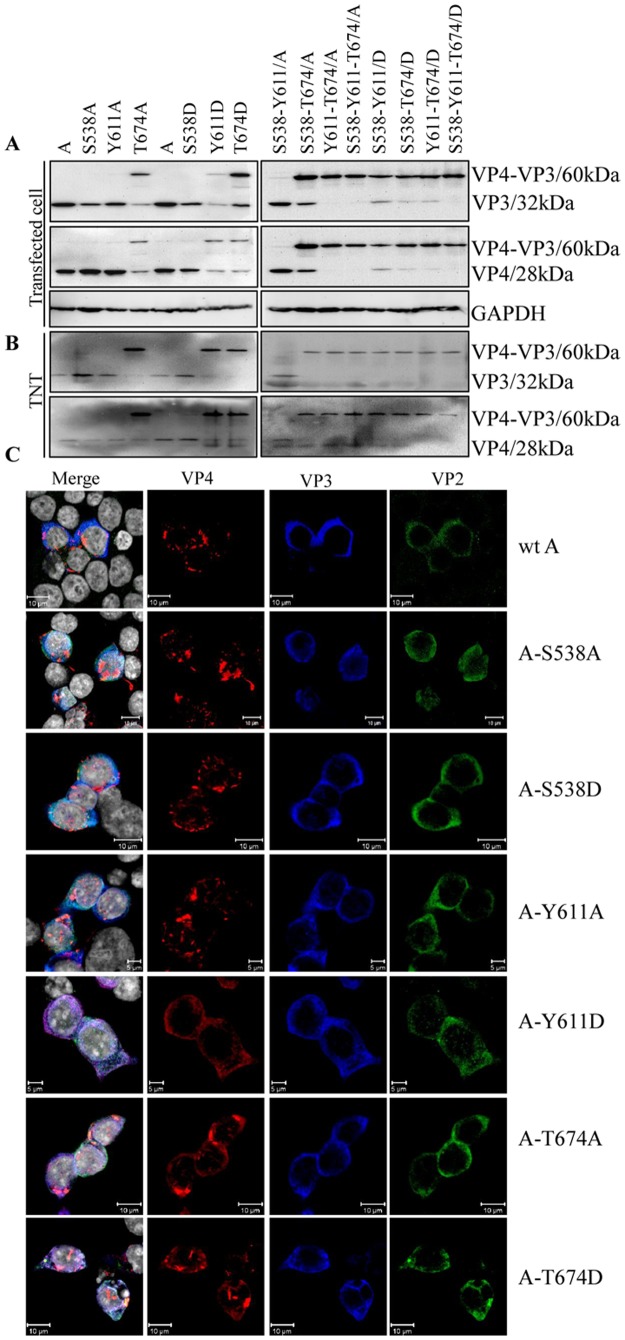
Fig 5. Analysis of proteolytic activity of viral VP4 protein.
(A) 293T cells were transfected with the recombinant wild-type A-segment plasmid or the Ala or Asp substituted A-segment plasmids at sites pSer538, pTyr611 and pThr674 within VP4. At 24 h post-transfection, cell samples were harvested and electrophoresed on 12% SDS-PAGE gels for Western blot analysis with mAbs specific to VP3 and VP4 proteins. GAPDH was used as a loading control. (B) Recombinant plasmids used in (A) were translated with the TNT T7 Quick Coupled Transcription/Translation System, and expressed proteins were detected with mAbs specific for VP3 and VP4 proteins. (C) Analysis of co-localization between IBDV-encoding proteins within segment A. 293T cells were transfected with the IBDV A-segment mutant with the single dephospho- and phospho-mimicking VP4 gene. Wild-type IBDV A-segment transfected cells were used as a positive control. At 24 h post-transfection, the cells were fixed and probed with chicken anti-VP2 pAb, mouse anti-VP3 mAb and rabbit anti-VP4 pAb followed by FITC-conjugated goat anti-chicken IgG (green), Alexa Fluor 647 donkey anti-mouse IgG (blue) and Alexa Fluor 546 donkey ant-rabbit IgG (red). Nuclei were counterstained with DAPI (grey). The cells were observed with a laser Zeiss LSM510 laser confocal microscope. Cells transfected with the A segment with the Tyr611Asp and Thr674 Ala/Asp substitutions revealed co-localization between the IBDV-encoded proteins.