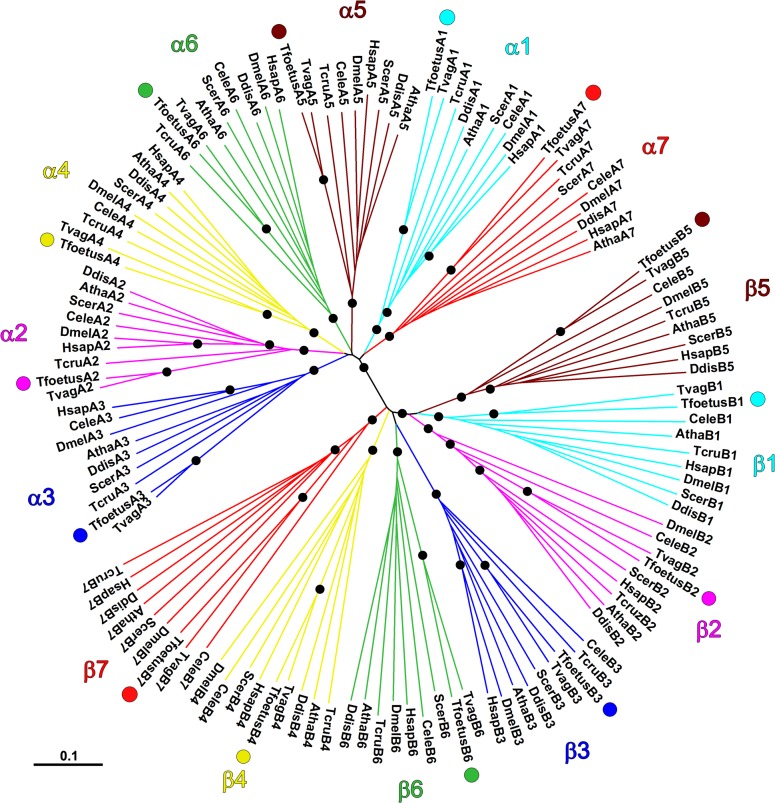
Fig 1. Phylogenetic analysis of the predicted 20S proteasome α- and β-type subunits from T. foetus.
The amino acid sequences of the 14 proteasome subunits identified in the T. foetus genome were aligned with their respective orthologues sampled from several eukaryotic species using CLUSTAL W algorithm. The unrooted phylogenetic tree was constructed by the neighbor-joining method based on the alignment using MEGA v. 5.2.2 software. The distance matrix was obtained by calculating p-distances for all pairs of sequences. Gaps were excluded using the pairwise-deletion option. Branch points were tested for significance by bootstrapping using 1,000 replications. All seven α- and β-type subunits are marked and shown in different colours. The T. foetus 20S proteasome subunits are indicated with colourful dots. Nodes supported by high bootstrap results (≥ 95%) are indicated by black dots. Scale bar represents 0.1 substitutions per site. Organism abbreviations: Tvag, Trichomonas vaginalis; Tcru, Trypanosoma cruzi; Scer, Saccharomyces cerevisiae; Ddis, Dictyostelium discoideum; Cele, Caenorhabditis elegans; Atha, Arabidopsis thaliana; Dmel, Drosophila melanogaster; Hsap, Homo sapiens. See Table 1 and S1 Table for the accession numbers of the proteasome sequences.