Figure 4.
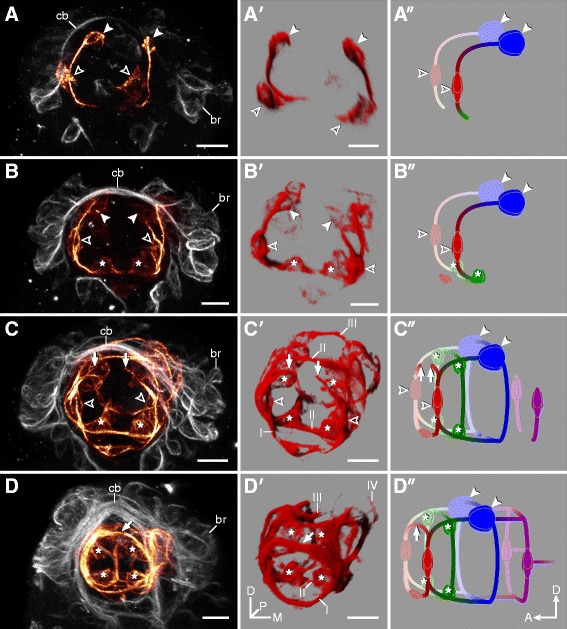
Development of the stomodeal nervous system in Hypsibius dujardini. Developmental series from earliest (A) to latest (D) embryonic stages. (A-D) CLSM projections showing the stomodeal nervous system (selectively colored in orange). Orientation as in (D′). Anti-acetylated α-tubulin immunolabeling. (A′-D′) Volume rendering of the corresponding structures. (A″-D″) Diagrammatic representation of the stomodeal nervous system in lateral view. Stomodeal commissures are numbered (I to IV). Note that neurons of the third stomodeal commissure (solid arrowheads) arise first (A) and project axons toward cells of the first commissure (hollow arrowheads), which only closes later in development (arrows in (C-C″), (D-D″)). The buccal sensory organs (asterisks in (B-B″), (C-C″), (D-D″)) contribute to the second commissure. Abbreviations: br, brain cells; cb, developing central brain neuropil (arising from a single commissure); D, dorsal; M, median; D, dorsal. Scale bars: (A-D), (A′-D′), 5 μm.
