Fig. 1.
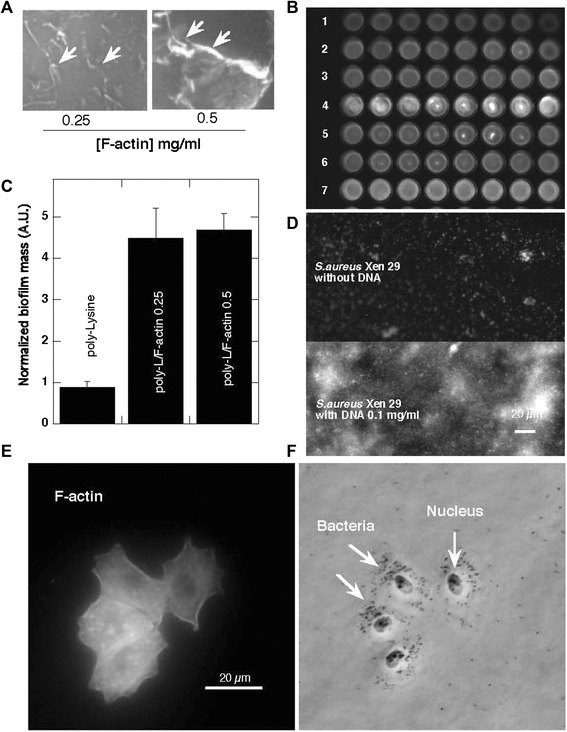
Bacterial biofilm formation in the presence of F-actin and DNA. a Arrows indicate F-actin filaments stained with rhodamine-phalloidin and attached to a glass slide coated with poly-Lysine (0.1% water solution). b Biofilm mass of Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 formed in the presence of F-actin. c Chemiluminescence of Pseudomonas aeruginosa Xen5 48 h after bacteria addition to LB broth (row 1) containing F-actin (rows 2, 3, 4) or DNA (rows 5, 6, 7) at concentrations of 0.01, 0.05 and 0.1 mg ml −1 respectively. d DNA staining (YOYO-1) of Staphylococcus aureus Xen29 biofilm after 48 h growth with and without the presence of DNA. e F-actin filaments of lung epithelial A549 cytoskeleton stained with rhodamine-phalloidin (cells were treated with 0.01% Triton X-100 for 10 min and washed 3x with PBS before staining). f Pseudomonas aeruginosa PAO1 cells preferentially attached to the cytoskeleton of A549 cell remnants
