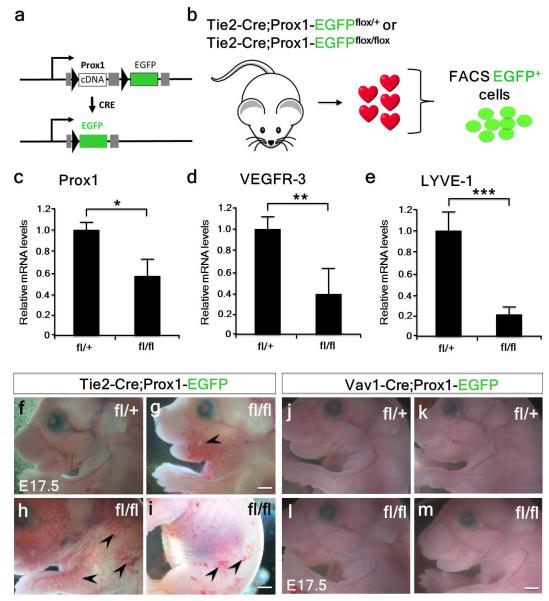
Extended Data Figure 7. Prox1 knockdown results in significantly decreased Vegfr3 and Lyve1 and TIE2-CreProx1fl/fl mutant embryos exhibit superficial vascular defects whereas Vav1-Cre;Prox1fl/fl mutants have a normal systemic vasculature.
Prox1 targeting via floxed excision of exon 1 and 2, results in EGFP expression thus labelling targeted cells (a). E17.5 hearts from either TIE2-Cre; Prox1fl/+ control embryos or TIE2-Cre; Prox1fl/fl mutants were grouped and digested to create a single-cell suspension for FACS (b). A total of 100,000 GFP+ cells were collected for each sample group. Relative gene expression was determined by qRT-PCR and revealed significantly decreased Prox1 (c; 0.59 fold), Vegfr3 (d; 0.39 fold) and Lyve1 expression (e; 0.22 fold); n=5 hearts per sample group, analyzed in triplicate; *p≤0.05; **p≤0.01; ***p≤0.001. All graphs are mean ± s.e.m. All statistics Students’t-test. Dissection of TIE2-Cre;Prox1fl/+ heterozygous (f; n=6) and TIE2-Cre;Prox1fl/fl mutant (g, h, i; n=9) littermate embryos at E17.5, revealed gross vascular anomalies in the fl/fl mutants (three examples shown in g-i), with evidence of ectopic surface blood vessels (g, ectopic vessels highlighted by black arrowheads), a disrupted vascular network (h) and either hemorrhaging (i; bleeding foci highlighted by black arrowheads) or blood-filled lymphatics, compared to littermate controls fl/+ (f). Vav1-Cre;Prox1fl/+ heterozygous (j, k; n=5) and Vav1-Cre;Prox1fl/fl mutants (l, m; n=8) revealed no obvious systemic vessel defects. Scale bars: g, i, m 100μm.