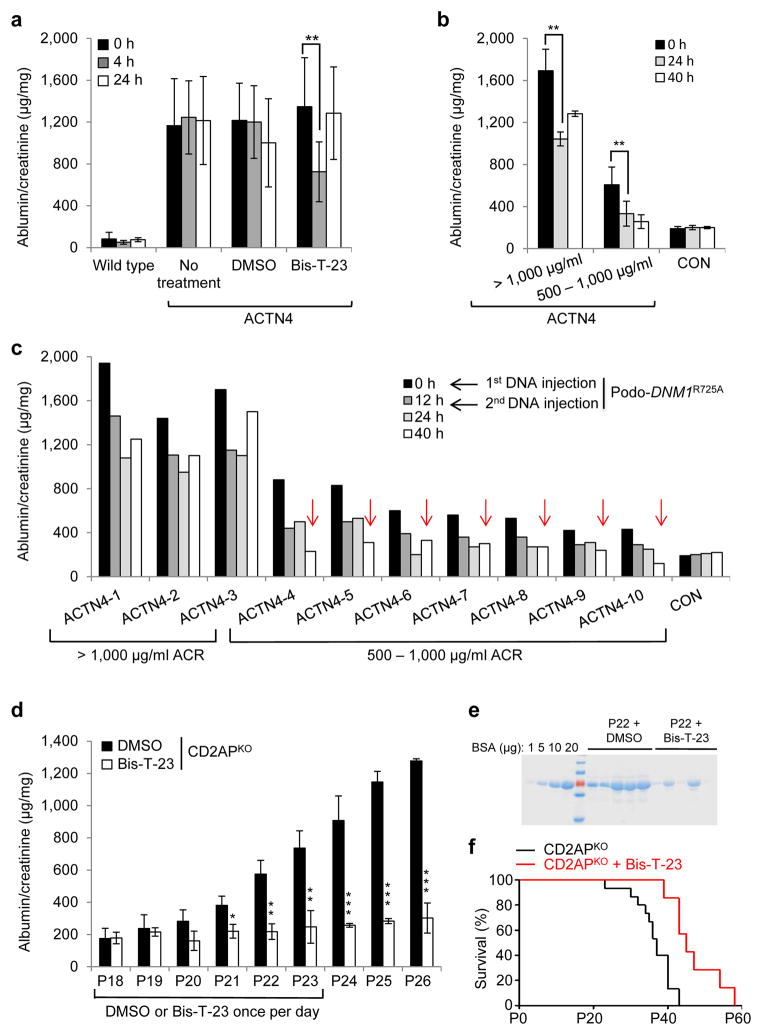
Figure 4.
Dynamin oligomerization targets actin cytoskeleton in podocytes. (a) Proteinuria in wild type and ACTN4 mice (without treatment or with treatment with either DMSO (1%, vehicle) or with Bis-T-23 (40 mg/kg)) as determined by spot urine test at indicated time points. Error bars, mean ± SD (**P ≤ 0.01, unpaired t-test). (b,c) Proteinuria in ACTN4 mice determined by spot urine test prior to and after double injection of a podocin-driven expression vector encoding DNM1R725A mutant protein. Animals were grouped by protein levels before treatment (n = 3 for > 1,000 μg/ml ACR; n = 7 for 500–1,000 μg/ml ACR). Individual animals from b are shown in c. Red arrows indicate reduction of proteinuria to control levels. Error bars, mean ± SD (**P ≤ 0.01, unpaired t-test). (d) Proteinuria in CD2APKO mice determined by spot urine test over several days during which animals were treated daily with DMSO (1%, vehicle) or Bis-T-23 (40 mg/kg), starting at Postnatal Day 18 (n = 5 mice per condition). Error bars, mean ± SD (*P ≤ 0.05; **P ≤ 0.01, ***P ≤ 0.001, unpaired t-test). (e) Coomassie blue staining of SDS-PAGE gel showing protein bands from two microliters of mouse spot urine at day 22 in d. BSA was used as a standard. (f) Line graph depicting number of live CD2APKO mice (black lines, n = 20 mice) and CD2APKO mice injected daily with Bis-T-23 (40 mg/kg) (red lines, n = 7 mice) at indicated time points. Animals exhibited a statistically significant difference in survival rate (log-rank: P < 0.0163).