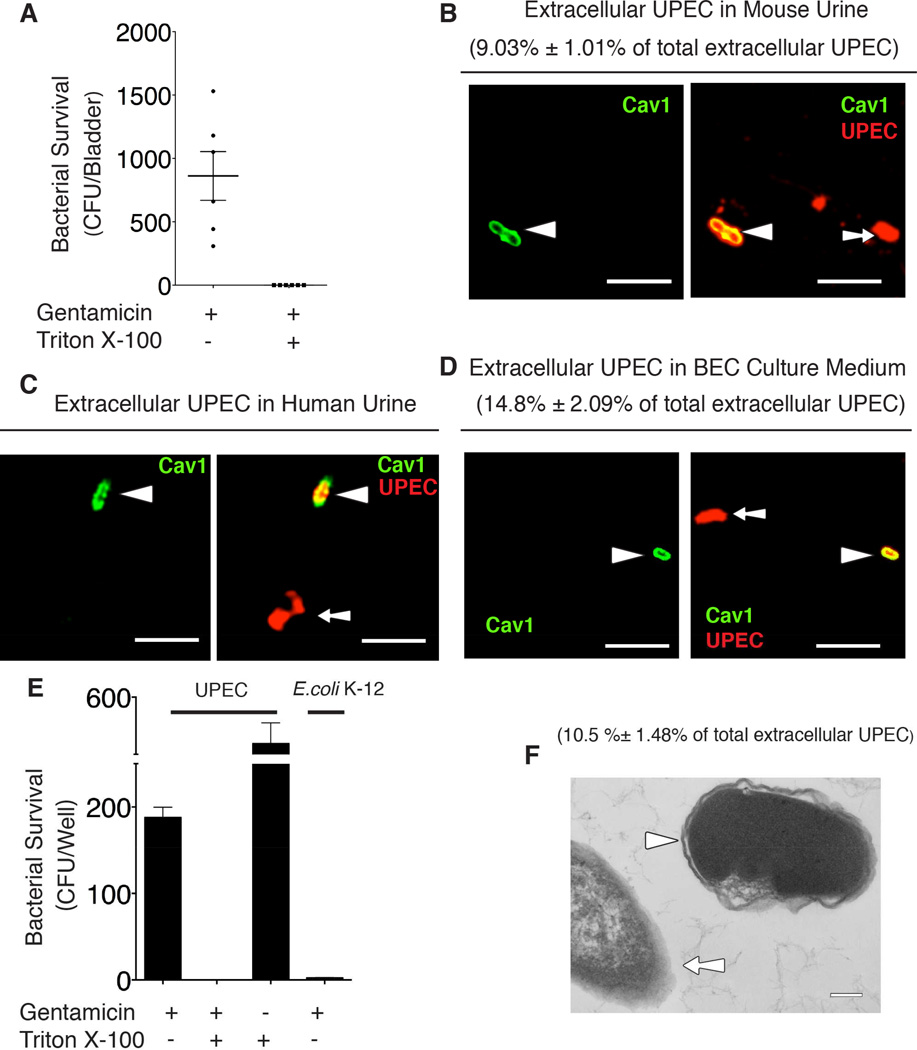
Figure 1. Expelled UPEC are encased in membrane-bound vesicles.
(A) Cell-free urine from infected C57BL/6 mice was collected at 6 hours post infection (h.p.i.), and treated with gentamicin with/without 0.1% Triton X-100 for 1hr. The surviving CFU were quantified. Error bars, SEM. n=9.
(B – D) Immunofluorescence staining for Caveolin-1 (green) and UPEC (red) in cell-free urine collected from infected mouse at 6 h.p.i (B), UTI patients (C), or culture medium collected from infected BEC line at 8 h.p.i. (D). Arrow depicts naked bacteria and arrowhead depicts vesicle-encased UPEC. The membrane-encased UPEC were quantified and expressed as the percentage of total examined UPEC shown in the parenthesis. Scale bar: 5 µm. n=3 slides.
(E) Bacterial viability assay performed on cell-free medium collected from BECs infected with UPEC strain CI5 or E.coli K-12 strain MG1655 at 8 h.p.i., and treated with gentamicin or 0.1% Triton X-100 alone, or gentamicin plus 0.1% Triton X-100 for 1 hour. Error bars, SEM. n=18.
(F) TEM image of extracellular bacteria collected from the culture medium of infected BECs. Arrowhead depicts vesicle-encased bacterium and arrow depicts a naked bacterium. The membrane-encased ECU were quantified and expressed as the percentage of total examined UPEC shown in the parenthesis. Scale bar: 0.2 µm. n=3 grids