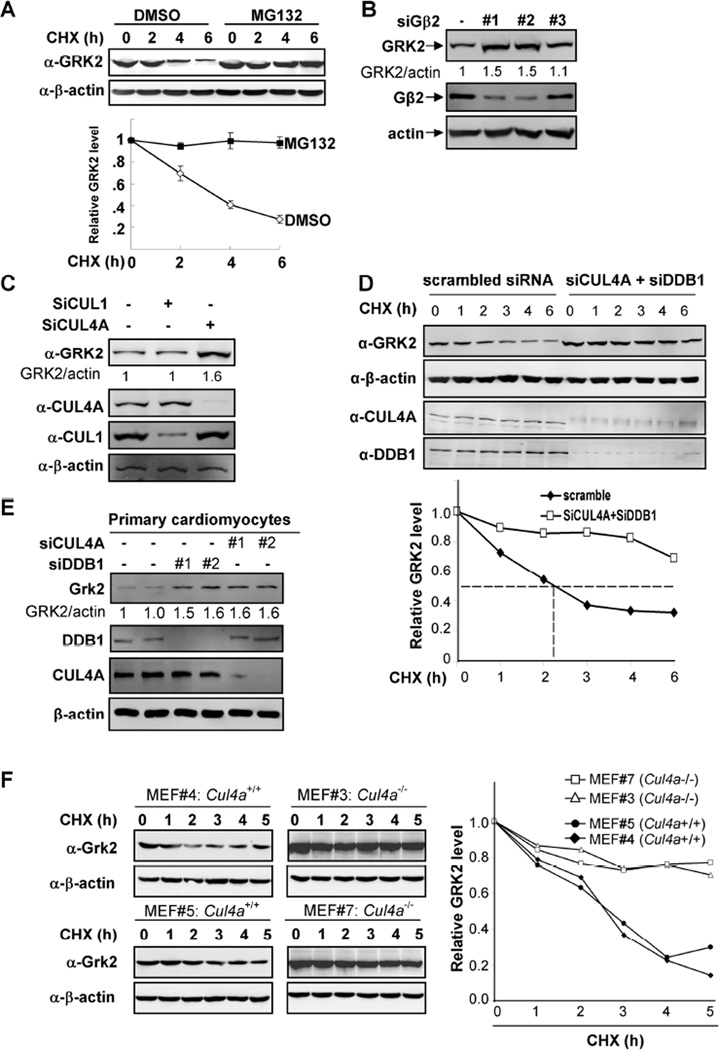
Figure 3. CRL4G|52 regulates the stability and steady state level of GRK2 protein.
(A) GRK2 is degraded by the 26S proteosome. HEK293 cells were treated wither either MG132 or solvent DMSO. The half-life of endogenous GRK2 protein was determined by cycloheximide (CHX)-chase.
(B, C) Knocking down of Gβ2 or CUL4A increases GRK2 protein level. HEK293 cells were transfected with three different siRNA oligo nucleotides targeting Gβ2 (B) or one targeting CUL4A (C). The GRK2 protein levels were determined by Western blotting and normalized against β-actin.
(D) GRK2 is stabilized by knocking down of both DDB1 and CUL4A. HEK293 cells were transfected with siRNA oligonucleotides targeting both CUL4A and DDB1. The half-life of GRK2 protein was determined by CHX treatment for different length of time as indicated and Western blotting with indicated antibodies.
(E) Knocking down Cul4a or Ddb1 increases Grk2 in rat primary cardiomyocyte cells. Two different siRNA oligos against either rat Cul4a or Ddb1 were transfected into rat cardiomyocyte cells.
(F) Deletion of Cul4a stabilizes GRK2 protein. The stability of GRK2 protein was determined in four littermate-matched MEFs by CHX treatment for different length of time as indicated and Western blotting with indicated antibodies.