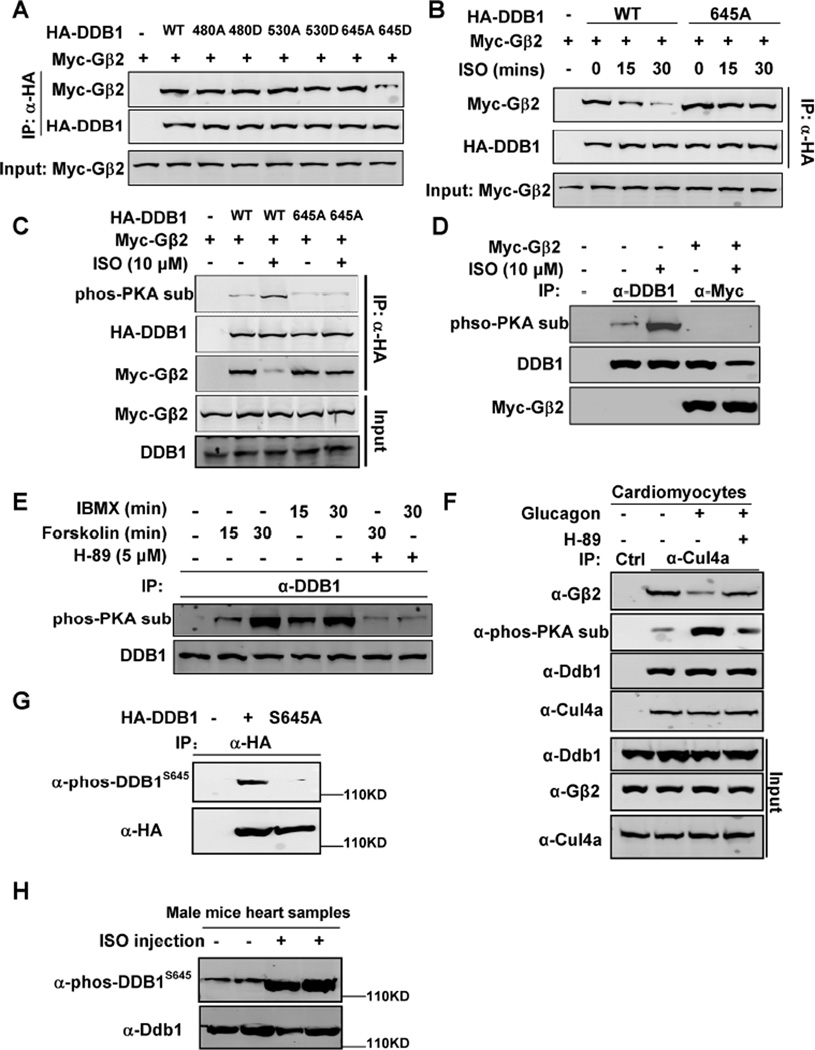
Figure 5. Gβ2-DDB1 complex is dissociated by PKA phosphorylation on DDB1 S645.
(A) DDB1645D mutant disrupts its binding to Gβ2. Myc-tagged Gβ2 and HA-tagged DDB1 or DDB1 mutant were transfected into HEK293 cells. The protein-protein interaction was determined by Co-IP and Western blot analyses.
(B) DDB1645A mutant blocks ISO effect on disrupting DDB1-Gβ2 binding. HEK293 cells were transfected with plasmids expressing Myc-Gβ2 and HA-DDB1/645A mutant, and then treated with ISO, followed by Co-IP and WB.
(C) ISO induces phosphorylation of the wild type DDB1 but not DDB1645A mutant. Myc-tagged Gβ2 and HA-tagged DDB1 or DDB1 mutant were transfected into HEK293 cells and then treated with ISO. The individual proteins were immunoprecipitated and subjected to Western blot with indicated antibodies.
(D) Gβ2 only binds to un-phosphorylated DDB1. Myc-tagged Gβ2 were transfected into HEK293 cells and then treated with ISO. The Myc-Gβ2 was immunoprecipitated and Western blot was performed to detect the co-precipitated DDB1.
(E) IBMX and Forskolin induce endogenous DDB1 phosphorylation. HEK293 cells were treated with IBMX, Forskolin, and H-89, as indicated. The individual proteins were precipitated with indicated antibodies and detected by Western blot analyses.
(F) Glucagon treatment in cardiomyocytes also induces DDB1 phosphorylation and disrupts DDB1- Gβ2 binding.
(G) Wild-type, but not S645A mutant, DDB1 was detected by anti-phos-DDB1S645 antibody.
(H) ISO induced DDB1 phosphorylation at S645 in vivo. 4 littermate-matched male mice were injected ISO as described, and their heart samples were harvested for Western blots analyses.