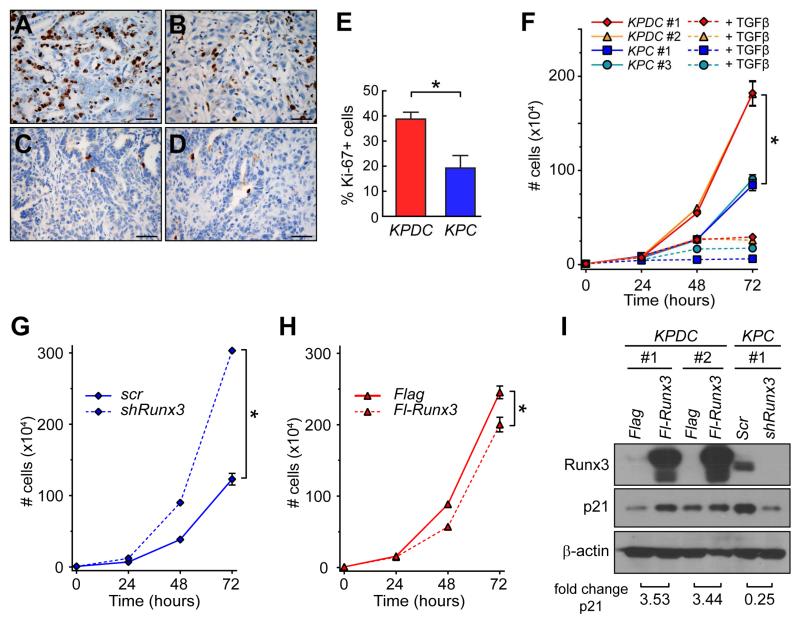
Figure 5. Runx3 inhibits proliferation in invasive PDA cells.
(A and B) Ki-67 expression in autochthonous (A) KPDC and (B) KPC PDA.
(C and D) Cleaved caspase 3 in autochthonous (C) KPDC and (D) KPC PDA.
(E) Proliferation in autochthonous KPDC and KPC tumors (mean ± SEM, *p<0.05).
(F) Proliferation of purified PDA cells ±TGFβ in vitro (n=3, mean ± SEM; *p<0.001).
(G) Proliferation of control (Scr) and Runx3-knockdown (shRunx3) purified primary KPC cells in vitro (n=3, mean ± SEM; *p<0.001).
(H) Proliferation of control (Flag) and Runx3-overexpressing (Fl-Runx3) purified KPDC cells in vitro (n=3, mean ± SEM; *p<0.001).
(I) Immunoblots for p21 in control and Runx3-overexpressing KPDC cells and control and Runx3-depleted KPC cells. Fold changes were quantified by densitometry and normalized to actin. Scale bars, 50 μm.