Figure 2.
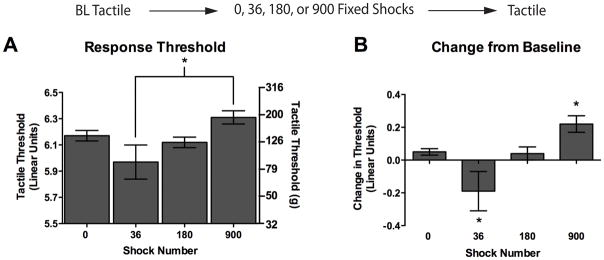
Brief exposure to fixed spaced stimulation causes mechanical hyperreactivty, while an extended exposure causes hyporeactivity. Tactile reactivity was assessed after rats received 0, 36, 180, or 900 fixed legshocks. Assessments were made at 30, 60, and 180 min following legshock. Because time was not a significant factor in our analysis we collapsed across this variable and present mean data. (A) Mean absolute tactile thresholds after shock treatment. The left y-axis depicts linearized data while the right y-axis depicts the gram force equivalents. (B) Mean change from baseline scores. Asterisks indicate statistically significant differences (p < .05), and error bars depict ± SEM. The inset depicts the experimental design.
