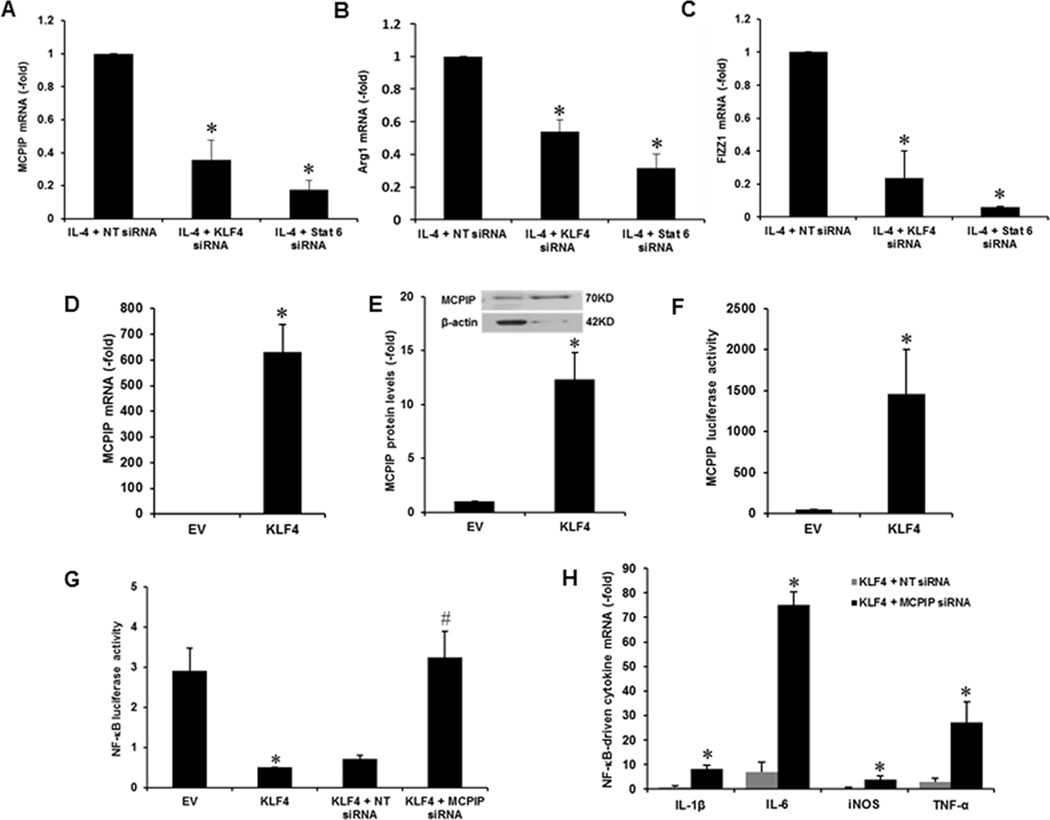
FIGURE 3.
IL-4-induced MCPIP induction is via STAT6/KLF4, and KLF4 induced NF-κB inhibition is mediated via MCPIP. The peritoneal macrophages isolated from C57BL/6 mice were pretreated with siRNA against KLF4 and STAT6 for 24 hr, and then treated with IL-4 (20ng/ml) for 4 hr. Expression of MCPIP and M2 markers (Arg1, FIZZ1) was determined by qRT-PCR (A, B, C). Transfection with KLF4 expression plasmid induced MCPIP expression in murine macrophages as determined by qRT-PCR (D) and western blot (E). Murine macrophages were transfected with MCPIP promoter-luciferase construct with or without co-transfection with KLF-4 expression vector for 24hr and luciferase activity was measured in the lysate. Expression of KLF4 enhanced MCPIP-luciferase reporter activity (F). Mouse macrophages were pretreated with siRNA against MCPIP for 24 hr then treated with 100ng/ml of LPS for 6 hr. KLF4 suppression of LPS-induced NF-κB activity was prevented by siRNA knockdown of MCPIP as measured by the NF-κB reporter kit (G). KLF4 suppression of LPS-induced NF-κB target genes (iNOS, IL-1β, TNF-α, and IL-6), assayed by qRT-PCR, were prevented by siRNA knockdown of MCPIP (H). *P <0.05 vs untreated Control cells, #P <0.05 vs non-targeted (NT) siRNA. Experiments were repeated three times.