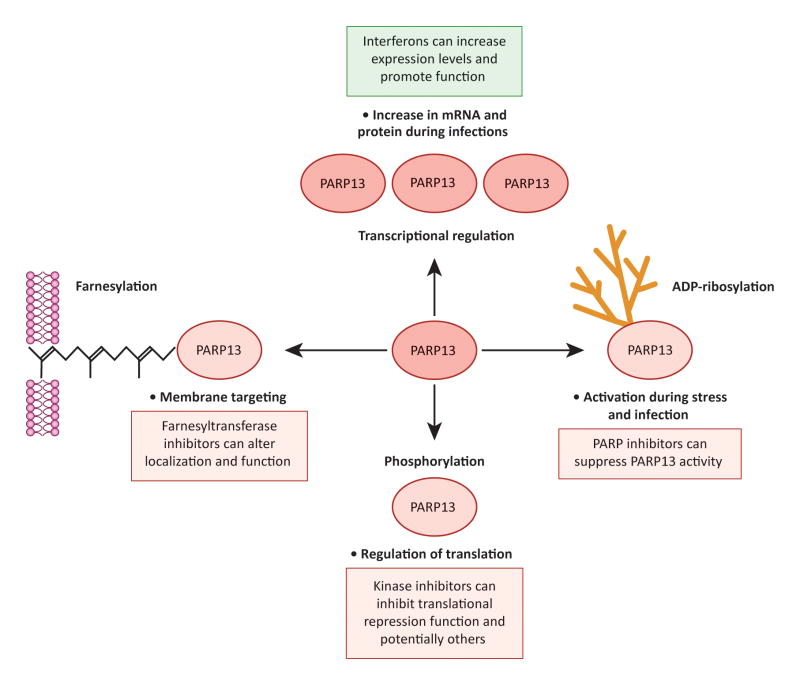
Figure 4. Mechanisms of PARP13 regulation.
Bullet points indicate how the indicated regulation affects PARP13 levels and activity; boxed text indicates how inhibition (red) or activation (green) of these regulatory mechanisms can be used therapeutically. Clockwise: 1) PARP13 expression is upregulated at the level of transcription by interferons. 2) PARP13 is poly(ADP-ribos)ylated by another member of the PARP family; ADP-ribosylation of PARP13 increases during stress and infection, and likely increases PARP13 activity. 3) PARP13 is phosphorylated at multiple residues by GSK3β; phosphorylation promotes the translational repression function of PARP13. 4) PARP13.1 is farnesylated at Cys899, a modification that results in its anchoring to cellular membranes.