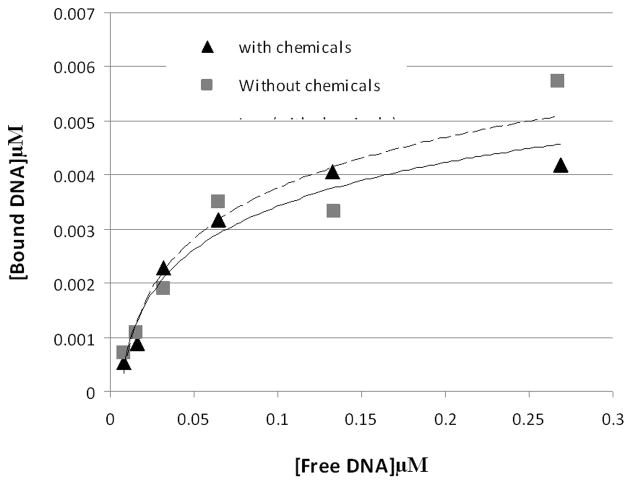
Figure 2. The chemistry also has minimal effect on the DNA-binding or affinity of purified GFP-C/EBP.
To 45 μl of 0.31 mg/ml (~8.2 μM) purified GFP-C/EBP in buffer KP (0.1 M potassium phosphate, pH 6.8) was added 5 μl 10 mM NaIO4. The mixture was wrapped in foil and incubated in the dark for 30 min. on a rocking platform. 5 μl of 10 mM Na2S2O5 was added and incubation continued an additional 30 min and then 36 μl of buffer KP was added (0.155 mg/ml final). Similarly, 25 μl 2 μM radiolabeled rEP18 in buffer KP was treated with 2.5 μl of each reagent and diluted with 61 μl of buffer KP (0.82 μM final). The 90 μl of reacted GFP-C/EBP was mixed with 54 μl buffer GS, 18 μl of 0.5 mg/ml poly dI:dC, and 18 μl H2O and 20 μl of this mixture was incubated with 10 μl of the rEP18 or serial 1:2 dilutions of it in buffer KP for 30 min at room temperature, 5 μl of BPB-Glyc (0.015% bromophenol blue, 50% glycerol) was added and 20 μl was loaded onto 5% native PAGE for gel shift assay. During incubation, the concentration of GFP-C/EBP was 77 μg/ml and the DNA concentrations are shown in the graph. Without chemicals (squares, dashed line), the line is generated using the equation [Bound] = 0.004 x Ln [Free] + 0.0162, R2 = 0.91; with chemicals (triangles, solid line), the line is generated using [Bound] = 0.0035 x Ln [Free] + 0.0145, R2 = 0.96.