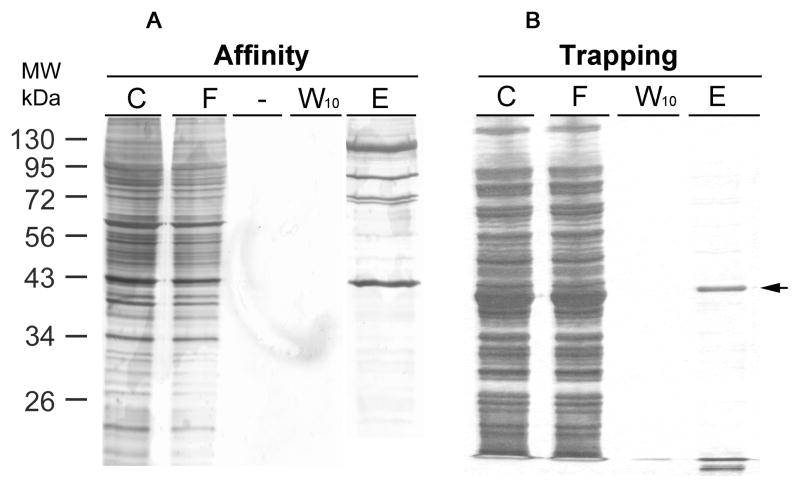
Figure 3. Comparing GFP-C/EBP purity from affinity chromatography and trapping methods.
Bacterial (BL21) crude extract containing fusion protein GFP-C/EBP was used as a model to compare purity by affinity chromatography or trapping methods. A, For affinity chromatography, UltraLink Hydrazide resin was first coupled with rEP18. Briefly, 5 μL of 100 μM rEp18 oligonucleotide and 85 μL of buffer KP was reacted with 10 μL of 10 mM sodium metaperiodate in the dark for 30 minutes at room temperature. The reaction was quenched by addition of 10 μL of 10 mM sodium metabisulfite for 10 minutes at room temperature. The mixture was desalted on a 1 ml P-6 spin column to remove any unreacted chemicals. This aldehyde form of rEP18 DNA was mixed with a 200 μL UltraLink Hydrazide resin slurry (1:1), which was pre-washed thrice with buffer KP. After two-hour coupling at room temperature on a rotating wheel, the resin was washed with TE0.1 thrice, and incubated with 100 μL of bacterial extract (C) in a final 1.0 mL volume at 4°C for 30 minutes with gentle mixing. And then, the mixture was packed in a chromatographic column for collecting flow through (F). Following ten wash (0.5 mL each) with TE0.1, the last wash was collected (W10), and the packed resin was eluted by TE0.5 buffer (E). B, For trapping the aldehyde form of rEP18 was prepared as in panel A was mixed with bacterial extract in a final volume of 1 ml for 30 min. on a rocker at room temperature. The mixture was then combined with the hydrazide resin, and incubated for two-hour at room temperature before packing in a column. Column washing and elution were the same as in panel A. For both experiments, each fraction (20 μL) was loaded on a 12% SDS PAGE, and the proteins were stained by silver. The arrow to the right shows the position of the GFP-C/EBP purified by Ni2+-NTA-agarose.