Figure 1.
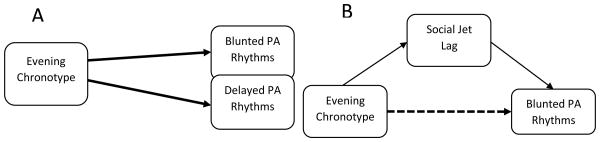
Depiction of the study model. A. Depicts the main hypotheses predicting evening chronotype leading to blunted and delayed positive affect (PA). B. Depicts additional study aim of investigating social jet lag as a potential mediator in the relationship between evening chronotype and blunted PA rhythms.
