Figure 2.
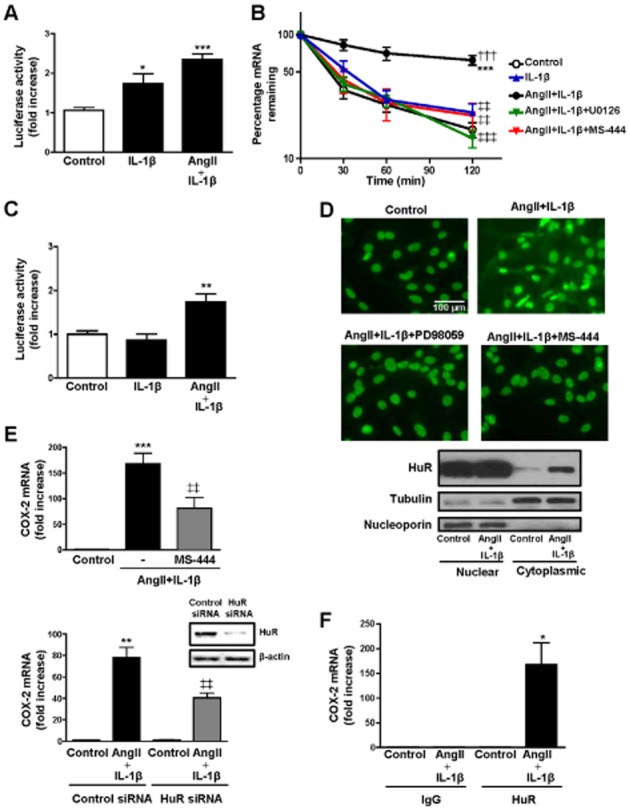
The synergistic effect of AngII and IL-1β on COX-2 expression in VSMCs is due to an increase in COX-2 mRNA stability mediated by HuR. (A) Luciferase activity in VSMCs transfected with a luciferase reporter construct containing the COX-2 promoter and incubated with vehicle (control), IL-1β or AngII + IL-1β for 4 h. (B) Effect of AngII + IL-1β on COX-2 mRNA stability (24 h after stimulation) and the inhibition of this effect by ERK1/2 (U0126) and HuR (MS-444) inhibitors. Actinomycin D, a transcriptional inhibitor, was incubated during the indicated times, after which COX-2 mRNA levels were measured by qPCR. (C) Luciferase activity in VSMCs transfected with a luciferase reporter construct containing COX-2 3′-UTR and incubated with vehicle (control), IL-1β or AngII + IL-1β for 4 h. (D) Effect of PD98059 (ERK1/2 inhibitor) and MS-444 on HuR subcellular localization assayed by HuR immunofluorescence and Western blotting of cellular fractions from VSMCs stimulated with AngII + IL-1β for 24 h. (E) Effects of MS-444 and HuR siRNA on COX-2 mRNA levels in VSMCs stimulated with AngII + IL-1β for 24 h. Representative blots of six independent experiments of HuR expression in cells transfected with control siRNA or HuR siRNA are included. (F) Ribonucleoprotein immunoprecipitation of HuR or control IgG was performed to isolate mRNA bound by HuR in VSMCs stimulated with AngII + IL-1β for 24 h. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 versus control; †††P < 0.001 versus IL-1β; ‡‡P < 0.01, ‡‡‡P < 0.001 versus AngII + IL-1β. n = 4–8.
