Fig. 1.
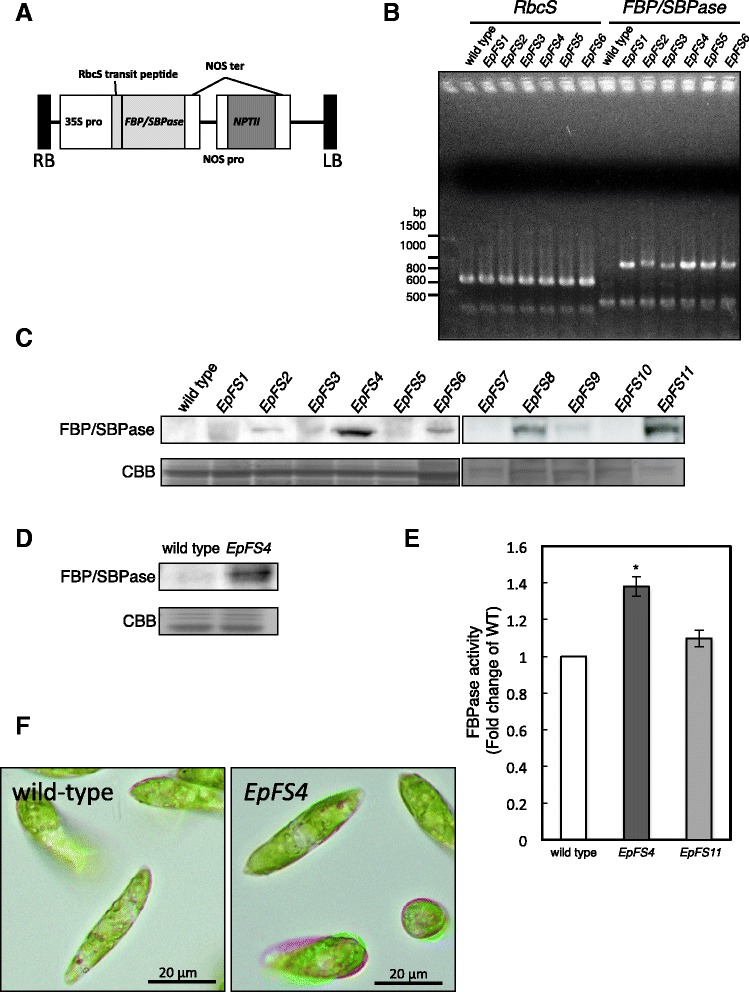
Isolation of transgenic E. gracilis cells having the FBP/SBPase gene. The construct structure of the gene using transformation of Euglena cells (a). Genomic PCR amplification of endogenous rbcS (637 bp) and FBP/SBPase (937 bp) genes from the wild-type and transgenic (EpFS) cell lines of E. gracilis (b). Western blot analysis of the crude extracts from wild-type and EpFS cell lines (c) and the intact chloroplastic fractions from wild-type and EpFS4 cells (d) using an antibody raised against the FBP/SBPase protein. Total FBPase activity in the stationary phase wild-type and EpFS cell lines grown under normal conditions (e). The photographs of wild-type and EpFS4 cells grown under normal conditions (f). Values are indicated as the mean ± standard deviation for three individual experiments. An asterisk indicates significant differences from the wild-type E. gracilis cells (*P < 0.05)
