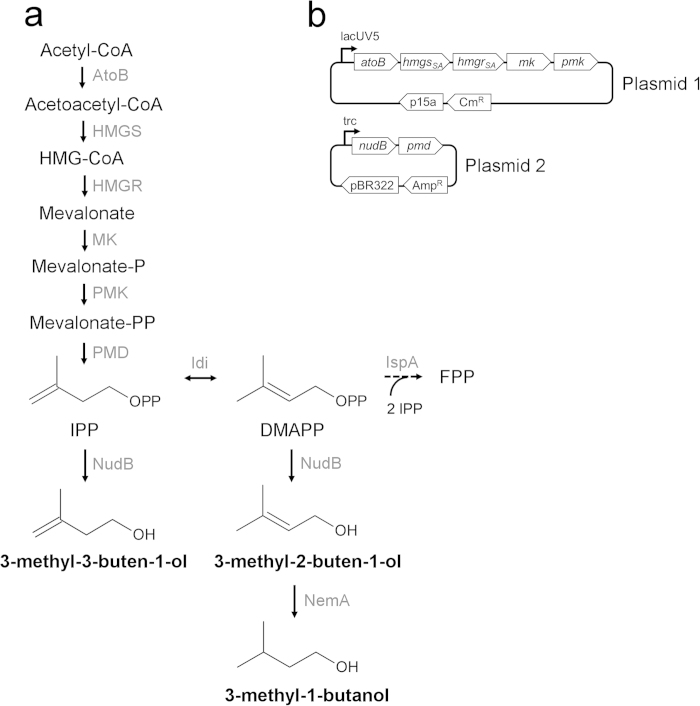
Figure 1. A heterologous MVA pathway for C5 alcohol production.
(a) Pathway overview. The heterologous mevalonate pathway in E. coli consists of 7 reactions to convert acetyl-CoA into IPP and DMAPP. Dephosphorylation of these compounds by NudB, a promiscuous E. coli phosphatase, produces 3-methyl-3-buten-1-ol and 3-methyl-2-buten-1-ol, respectively. NemA, an endogenous reductase, is capable of reducing 3-methyl-2-buten-1-ol, but not 3-methyl-3-buten-1-ol, into fully reduced 3-methyl-1-butanol. (b) Plasmid architecture. A two plasmid system for 3-methyl-3-buten-1-ol production served as the initial engineering platform (strain KG1). Plasmid 1 contained genes from atoB to PMK with a medium copy p15A ori and weak lacUV5 promoter16. Plasmid 2 contained nudB and PMD with a high copy pBR322 ori and strong trc promoter. To produce mixed alcohols, a fusion protein and reductase were expressed on plasmid two (see Fig. 4).