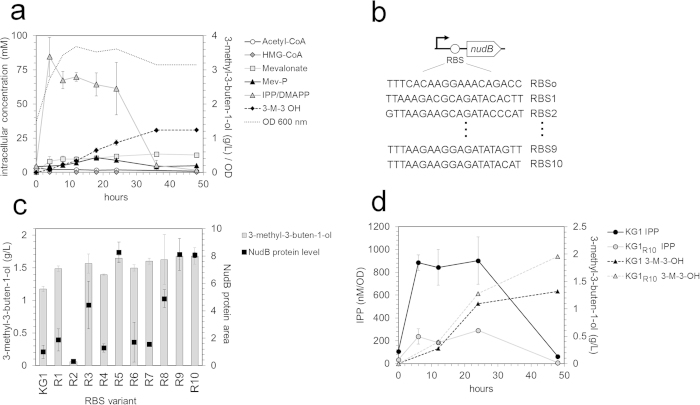
Figure 2. RBS engineering to improve 3-methyl-3-buten-1-ol titer and reduce IPP accumulation.
(a) Metabolite profiling of strain KG1. Mevalonate pathway intermediates were quantified in strain KG1 over a 48 hour time-course by LC-MS, showing IPP as the highest accumulating intermediate by a factor of 8. A growth curve for strain KG1 is shown as a dashed line. Error bars represent standard deviation (n = 3). 3-M-3-OH = 3-methyl-3-buten-1-ol. (b) RBS optimization of nudB. Ten RBS variants of nudB (see Table S1) were generated using RBS calculator and cloned into plasmid 2, forming JPUB-004498 to JPUB-004507. (c) 3-Methyl-3-buten-1-ol titer and NudB protein level in KG1R1 – KG1R10. Strains containing nudBRBS1 through nudBRBS10 (KG1R1 - KG1R10) were assayed for 3-methyl-3-buten-1-ol and NudB protein level. Bars represent 3-methyl-3-buten-1-ol titer after 36 hours. Squares show NudB protein area at 24 hours relative to that measured in strain KG1 (normalized to a value of 1). Error bars represent standard deviation (n = 3). (d) IPP accumulation and 3-methyl-3-buten-1-ol production in strains KG1 and KG1R10. IPP concentrations in KG1R10 were reduced by 4-fold relative to KG1, while 3-methyl-3-buten-1-ol titer increased by 60%. Error bars represent standard deviation (n = 3).