Figure 4. Antigenic site Ø.
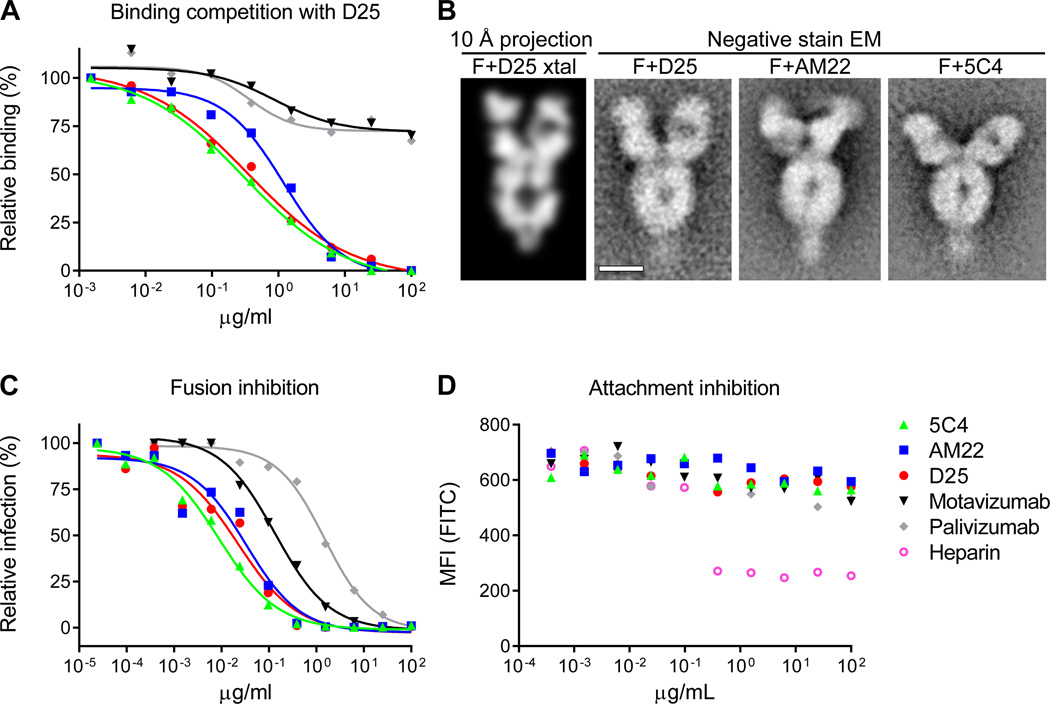
Highly effective RSV-neutralizing antibodies target a site at the membrane-distal apex of the prefusion F trimer. (A) The ability of antibodies to block D25 binding to RSV-infected cells was measured as a function of antibody concentration. (B) Analysis of RSV F-Fab complexes by negative stain electron microscopy: Reprojection of a 12 Å slice through the crystal structure of RSV F + D25 Fab filtered to 10 Å resolution (left). A slice was used to emphasize visibility of the F glycoprotein cavity. Aligned average of 263 particles of RSV F + D25 Fab (middle - left). Aligned average of 550 particles of RSV F + AM22 Fab (middle - right). Aligned average of 171 particles of RSV F + 5C4 Fab (right). Scale bar is 50 Å. (C) Fusion inhibition and (D) attachment inhibition activity for antibodies targeting antigenic site Ø and F-specific antibodies targeting other antigenic sites. For the attachment-inhibition assay, heparin was used as a positive control. Data in panels (A) (C) and (D) are representative of multiple independent experiments.