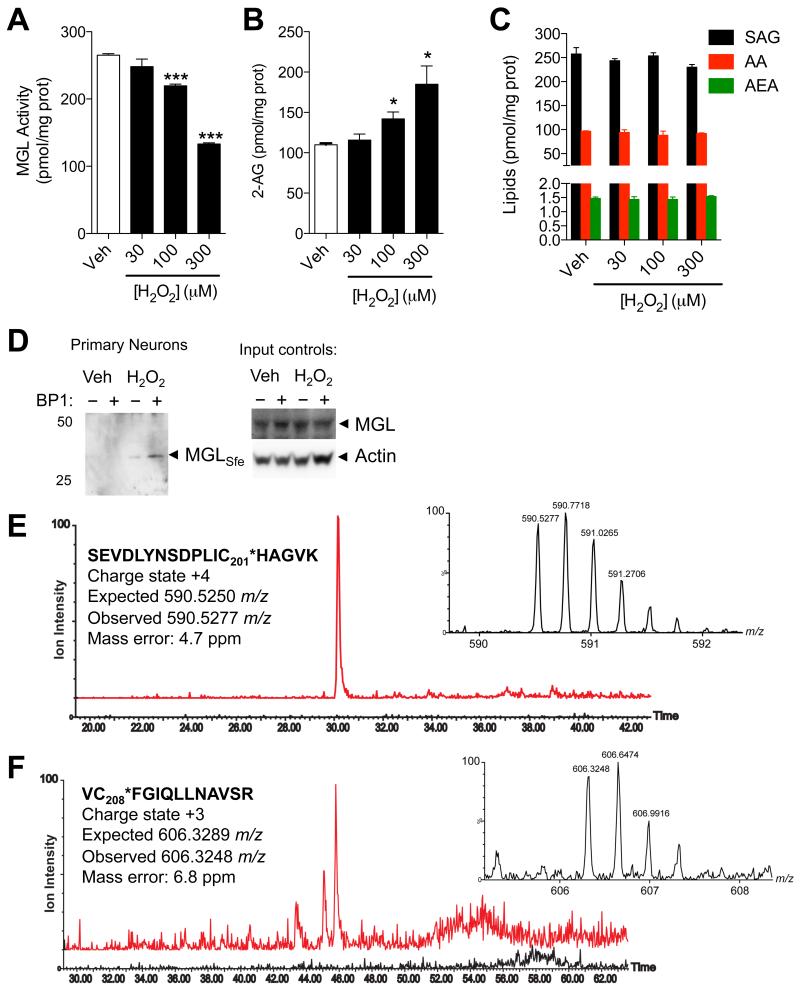
Figure 4. Peroxide-dependent inhibition of MGL activity and 2-AG accumulation in brain neurons.
(A-D) Effects of H2O2 (filled bars) or vehicle (open bars) on (A) MGL activity, (B) 2-AG levels, and (C) 1-stearoyl,2-arachidonoylglycerol (SAG), arachidonic acid (AA), and anandamide (AEA) in rat cortical neurons in primary cultures. (D) Detection of sulfenylated MGL (MGLSfe) in primary cortical neurons in cultures after H2O2 treatment (300 μM, 1h). Sulfenylated MGL was trapped using the chemoselective probe BP1. Equal sample loading to the affinity precipitation was confirmed by measuring MGL (anti-MGL antibody) and actin (input controls). 50, 25: molecular weight size markers (kDa). (E) Ion current of the BP1-adduct of MGL peptide bearing C201 (590.53 m/z, z=4) extracted from the control incubation (black trace) and incubation of neurons with H2O2 (red trace). (F) Ion current of the BP1-adduct of MGL peptide bearing C208 (606.30 m/z, z=3) extracted from the control incubation (black trace) and incubation of neurons with H2O2 (red trace). In both E and F, the high-resolution mass spectra reported in the inset matches the expected charge state and m/z value. ***P<0.001 and *P<0.05 compared to vehicle, two-tailed Student’s t test.