FIGURE 6.
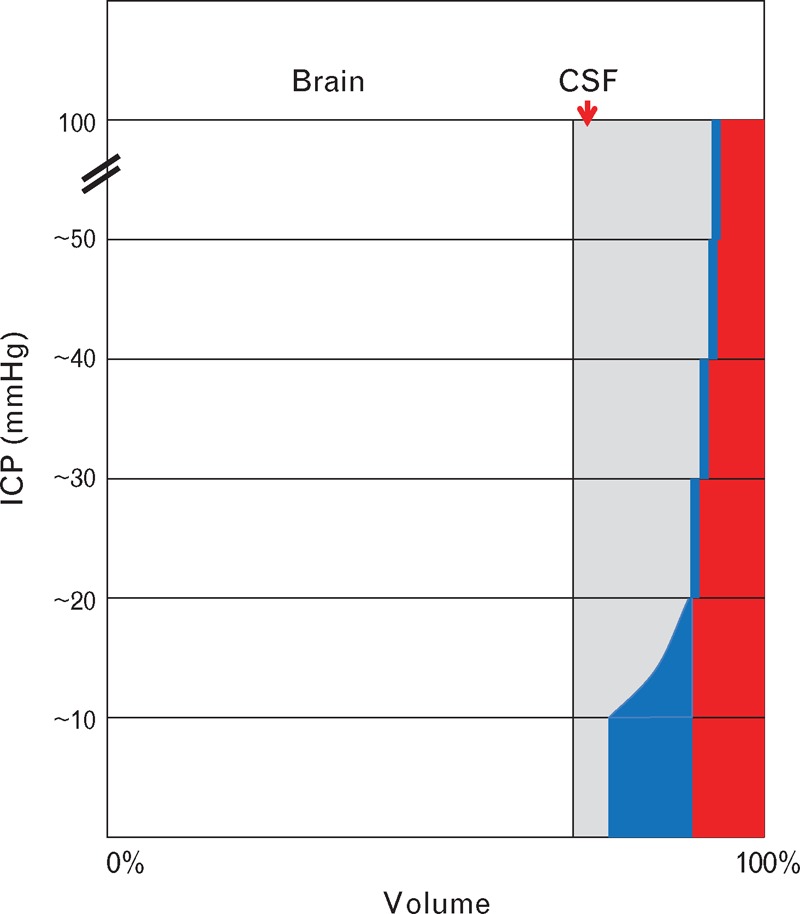
Illustration of Monro–Kellie principle. The cranium (and its extension into the spinal canal) has a fixed volume and contains four components: brain (and its extension as the spinal cord), cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), venous blood (blue), and arterial blood (red). If one component increases, another must decrease. Under normal conditions, intracranial pressure (ICP) is near atmospheric. If volume of a component rises (here CSF, but could be brain), there is progressive decrease in venous blood through venting from venous sinuses into the jugular vein in the neck. As pressure rises further, the veins are flattened and arteries are progressively narrowed.
