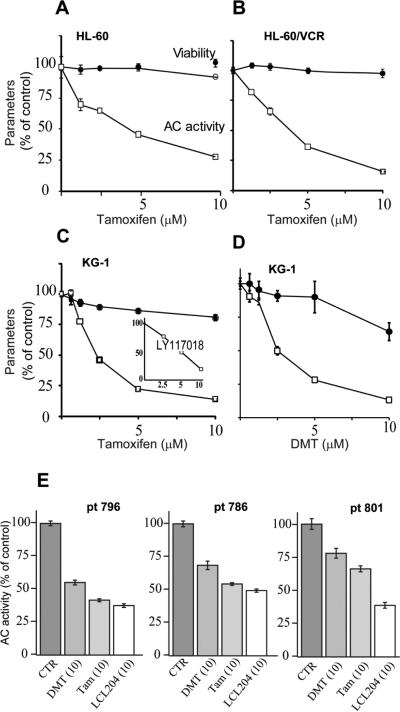
Fig. 1.
Effect of triphenylethylenes and AC inhibitor LCL204 on AC activity in cultured human AML cell lines and in AML cells derived from patients. (A-D) Cell lines. Cells (20,000/well) were seeded into 96-well plates in medium containing 10% heat-inactivated FBS one day prior to treatment. Tamoxifen, DMT, and raloxifene analog LY117018 were administered (in culture medium containing 1% FBS) for 24 hr at the concentrations indicated, and AC activity was then measured in intact cells using fluorescent substrate as detailed in Materials and Methods. Cell viability was measured at 24 hr in parallel experiments. n=6 for each experimental point; values are the mean ± S.E. Repeated experiments yielded like results. (E) Cells derived from patients. Cryo-preserved cells were thawed and viabilities assessed by trypan blue staining. Cells were seeded (30,000 live cells/well), and after 3 hr equilibration (tissue culture incubator), cells were treated as indicated for 4 hr. AC activity was then measured. n=5 wells per treatment; values are ± S.E. Micromolar concentrations in parentheses. CTR, control; DMT, N-desmethyltamoxifen; Tam, tamoxifen; pt, patient.