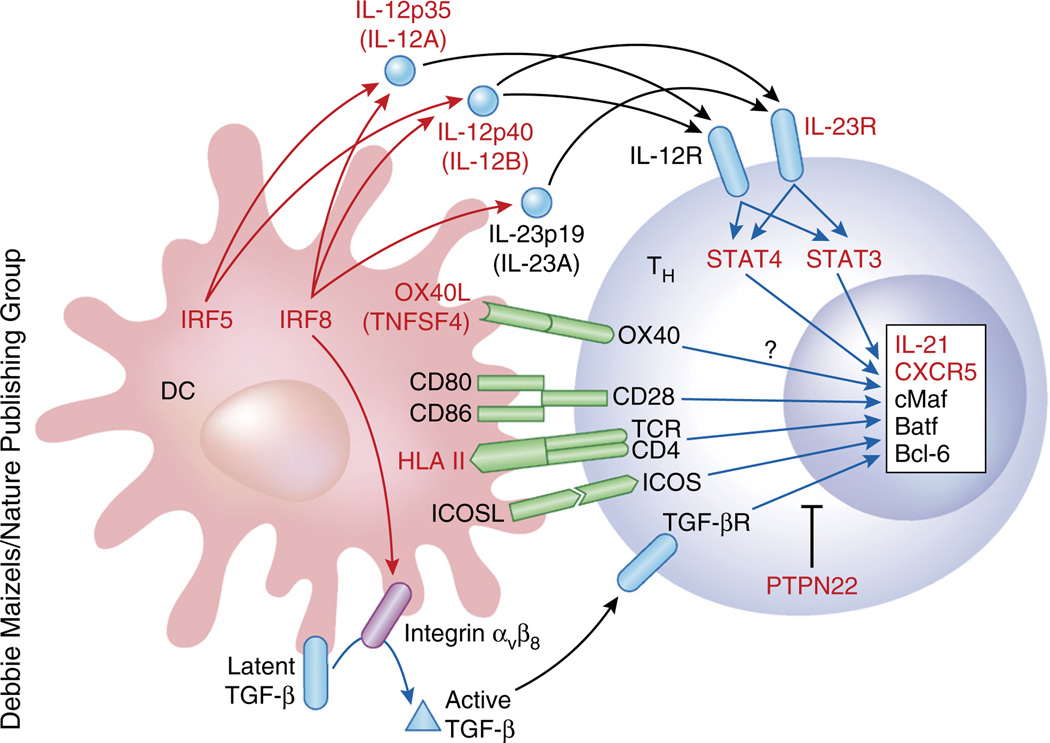
Figure 3.
Risk loci of human autoimmune diseases associated with the TFH developmental pathway. Multiple risk loci identified in GWAS in autoimmune diseases (indicated in red) are potentially associated with the regulation of the development and/or the function of human TFH cells. At least seven risk loci—IL12A, IL12B, IL23R, STAT3, STAT4, IRF5 and IRF8—are associated with IL-12 and IL-23. IRF8 also might contribute to TGF-β signaling by promoting the expression of TGF-β-activating integrin αvβ8 on the surface of DCs. Risk loci contain genes encoding TFH-specific molecules (such as IL21 and CXCR5), as well as genes associated with the inhibition of TFH cell development (such as PRDM1 and PTPN22). Whether and how these gene variants are associated with aberrant TFH responses in autoimmune diseases remains to be established.