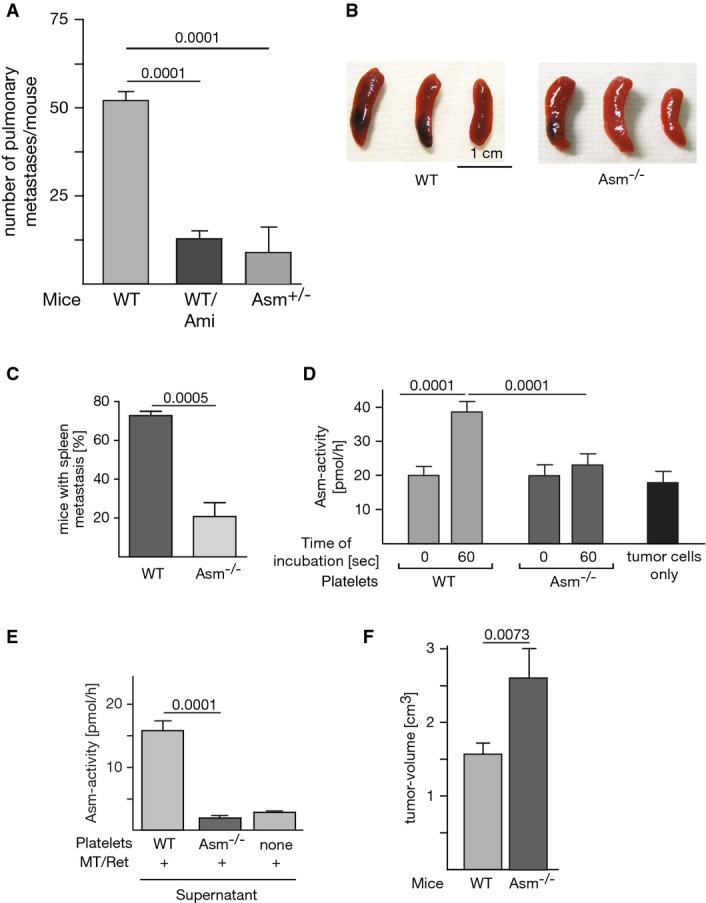
Targeting the Asm system prevents melanoma metastasis
A Amitriptyline (2 mg/kg, Ami) was intraperitoneally injected into C57BL/6 mice for five times every 12 h. Sixty minutes after the last injection, 1 × 105 B16F10 tumor cells were intravenously injected. Control experiments confirmed that amitriptyline inhibited Asm activity in the blood by approximately 85%. Asm heterozygous mice were injected with 1 × 105 B16F10 tumor cells. The number of lung metastases was determined after 14 days. Shown is the mean ± SD from six mice each, ANOVA followed by Tukey's test for multiple comparison. P-values are indicated.
B, C MT/ret cells (105) suspended in 200 μl Matrigel/PBS (1:1) were injected s.c. in the left and right flanks of 8-week-old Asm-deficient mice or wild-type mice. Mice were sacrificed at day 20 after injection, and spleens were inspected for the presence of metastases. The representative photographs (B) show the results from one of four experiments, and the quantitative analysis is displayed in (C).
D Platelets were isolated from wild-type or Asm-deficient mice by density-gradient centrifugation, and 1 × 107 platelets were incubated with 1 × 105 MT/ret melanoma cells. The samples were lysed, and Asm activity in cell lysates was determined. In unstimulated samples (time point 0 of co-incubation), tumor cell and platelet lysates were admixed after lysis.
E To measure secretion of Asm by platelets, tumor cells and platelets were co-incubated for 30 s, the samples were pelleted, the supernatants were acidified, and the Asm activity was measured. All Asm activity measurements were performed in the presence of 100 μM Zn2+.
F Local tumor growth in wild-type or Asm-deficient mice at the flank was measured at day 20.
Data information: Displayed is the mean ± SD of each three or four experiments. Statistical significance was determined by
t-test (C, E, F) or analysis of variance followed by Tukey's multiple comparisons test (D).
P-values are indicated.