Figure 8.
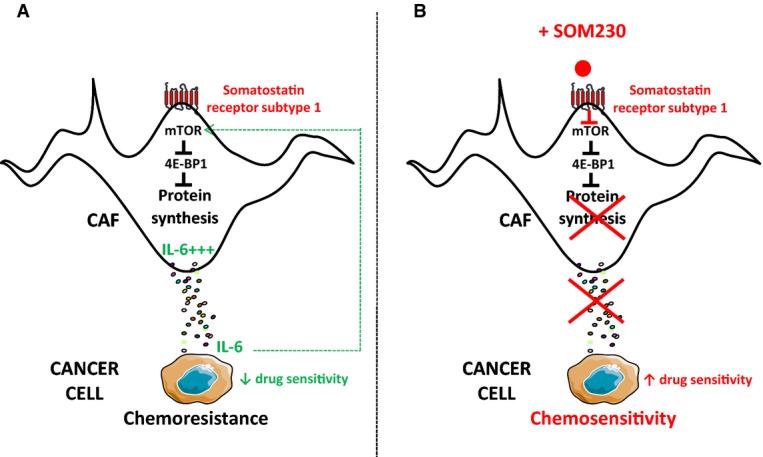
- Through the synthesis/secretion of soluble chemoprotective factors including IL-6, CAFs induce pancreatic cancer cell chemoresistance. High protein synthesis rate in CAFs is dependent on the robust intrinsic activation of the mTOR pathway resulting in inhibition of the protein translation inhibitor 4E-BP1. Secreted IL-6 participates in an autocrine feed-forward loop in the intrinsic activation of mTOR and subsequent high protein synthesis.
- CAFs express the somatostatin receptor sst1. Upon activation with the novel SOM230 somatostatin analogue (Pasireotide® Novartis) presenting a high affinity for sst1, the mTOR pathway is inhibited, resulting in reduced synthesis/secretion of chemoprotective factors including IL-6 through inhibition of mRNA translation. As consequences, the autocrine feed-forward IL-6/mTOR/protein synthesis/IL-6 loop is abrogated, and pancreatic cancer cells are re-sensitized to the apoptotic action of chemotherapies.
