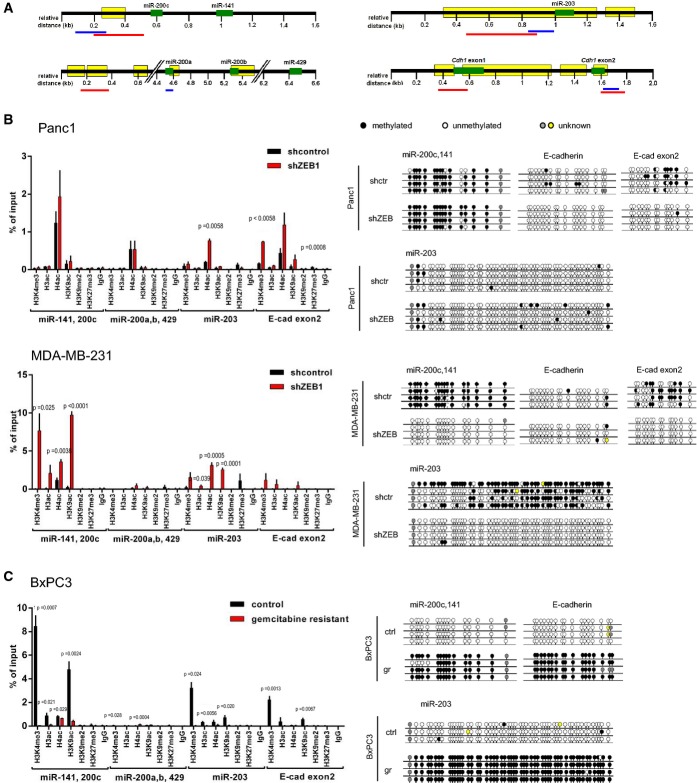
B, C Histone marks were analyzed using ChIP coupled to qRT–PCR for Panc1 control versus shZEB, MDA-MB-231 control versus shZEB (B), and BxPC3 control versus gemcitabine resistant (gr) (C). In MDA-MB-231 and Panc1, the active histone marks H3K4me3, H3ac, H4ac, and H3K9ac were enriched. Vice versa, in the drug-resistant clones of BxPC3, the active marks were reduced in the CpG islands. The repressive histone mark H3K27me3 was not detectable in the miR-200 loci, but in the loci of miR-203 and E-cadherin in Panc1 and MDA-MB-231. DNA methylation status was determined by bisulfite sequencing. Depletion of ZEB1 in MDA-MB-231 resulted in almost complete demethylation, whereas the selection of drug-resistant, ZEB1-expressing clones in BxPC3 induced complete methylation. n = 2 (Panc1) or 3 (MDA-MB-231 and BxPC3), mean ± SEM; unpaired Student's t-test.