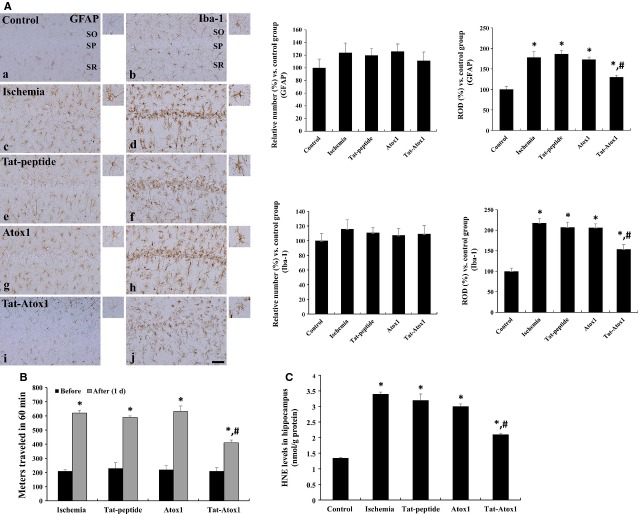
Figure 6.
Inhibitory effects of transduced Tat-Atox1 protein in ischaemic animal models. Immunohistochemistry for GFAP (a, c, e, g and i) and Iba-1 (b, d, f, h and j) in the CA1 region of the control (a and b), ischaemia (c and d), Tat peptide (e and f), Atox1 protein (g and h) and Tat-Atox1 protein-treated (i and j) groups 4 days after ischaemia/reperfusion (A). SP, stratum pyramidale; SO, stratum oriens; SR, stratum radiatum; bar = 50 μm. The locomotor activity in gerbils before and 1 day after ischaemia-reperfusion in ischaemia, Tat peptide, Atox1 protein and Tat-Atox1 protein-treated groups. Spontaneous locomotor activity is evaluated in terms of entire distance (metres) travelled before and 1 day after ischaemia-reperfusion (B) (n = 5 per group; *P < 0.05, significantly different from the before group, #P < 0.05, significantly different from the ischaemia group). The bars indicate standard error (SE). Analysis of HNE levels in the hippocampus of control, ischaemia, Tat peptide, Atox1 protein and Tat-Atox1 protein-treated groups at 3 hrs after ischaemia-reperfusion (C) (n = 5 per group, *P < 0.05, significantly different from the control group, #P < 0.05, significantly different from the ischaemia group). The bars indicate SE.