Fig. 10.
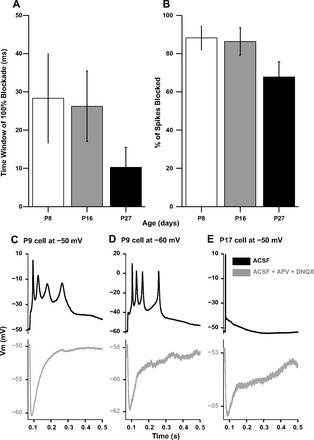
Potency of inhibition in suppressing spikes. A: time window of 100% action potential blockade by preceding IPSPs at P7–P9, P15–P17, and P22–P32, where the action potential was evoked by a depolarizing current pulse at varying intervals after synaptic stimulation. B: percentage of spikes blocked by IPSPs at P7–P9, P15–P17, and P22–P32, averaged over the time window of 0–50 ms preceding the current pulse onset. C: P9 neuron multiple spiking responses in normal aCSF (black trace, top) and in the presence of APV + DNQX (gray trace, bottom). D: the same P9 neuron as in C from a more hyperpolarized base potential. E: single spiking response of a P17 neuron in aCSF (black trace, top) and the underlying IPSP in aCSF + APV + DNQX (gray trace, bottom).
