Fig. 4.
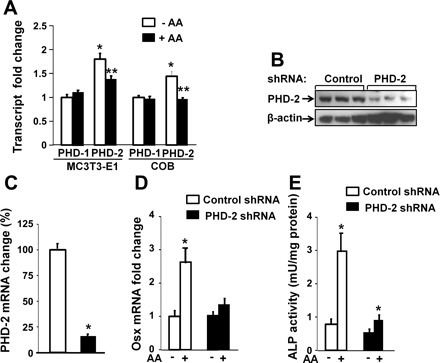
Knockdown of prolyl hydroxylase domain enzyme (PHD)2 expression impairs AA induction of Osx expression and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) activity in osteoblasts. A: isoforms of PHD1 and PHD2 expression in osteoblasts. MC3T3-E1 osteoblasts and primary mouse COBs were treated with 100 μg/ml AA or control vehicle for 24 h, followed by RNA extraction for real-time RT-PCR for measurements of relative expression levels of PHD1 and PHD2. The results are expressed as fold change over the expression level of PHD1 without AA treatment. *Statistical significance compared with expression level of PHD1 without AA treatment (P < 0.01, n = 3). **Statistical significance compared with expression level of PHD2 without AA treatment (P < 0.01, n = 3). B: PHD2 expression was reduced in MC3T3 cells expressing shRNA against PHD2, measured by Western blot. C: PHD2 mRNA expression was knocked down by lentivirus-mediated shRNA. MC3T3-E1 cells were transduced with lentivirus expressing shRNA specifically against PHD2 gene or scramble DNA sequence for 24 h. Cells were lysed for RNA extraction prior to real-time RT-PCR. *Statistical significance of expression levels in the cells infected with lentivirus-shRNA against PHD2 compared with the cells infected with lentivirus-shRNA against scramble DNA sequence (P < 0.01, n = 3). D: expression levels of Osx in lentivirus-shRNA transduced cells. MC3T3-E1 cells were transduced with lentivirus-shRNA as described in B. The cells were then treated with or without AA for 24 h and lysed for real-time RT-PCR. *Statistical significance of expression level in the cells treated with AA compared with in the corresponding cells without AA treatment (P < 0.01, n = 3). E: AA-induced ALP activity was significantly reduced in the cells expressing PHD2 shRNA. *P < 0.01 in cells treated with AA vs without AA. The magnitude of ALP induction in AA-treated PHD2 shRNA cells was significantly less compared with control shRNA cells.
