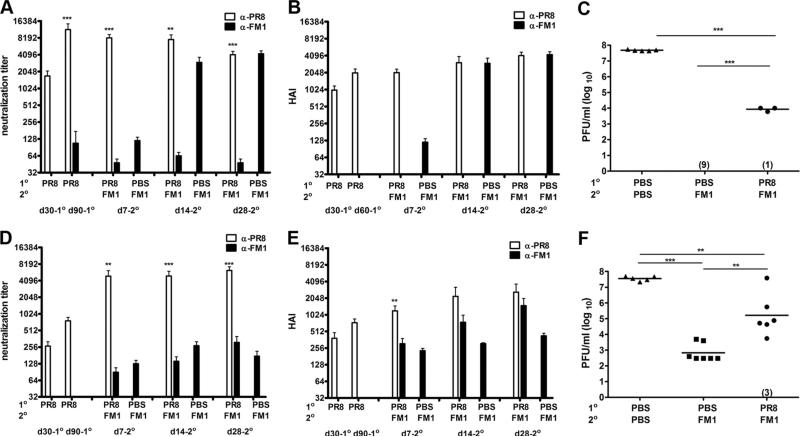
FIGURE 5.
Induction of original antigenic sin was independent of the interval between exposures to variant viruses. BALB/c mice (four to ten mice/group) were intranasally infected with 0.1 × LD50 of mouse-adapted PR8 (A–C) or i.m. immunized with 1400 HAU of whole inactivated PR8 (D–F). Three months later, PR8-infected or immune mice were infected with 0.1 × LD50 of mouse-adapted FM1 (A–C) or immunized with 1400 HAU of whole inactivated FM1 (D–F). Control mice (nine mice) were injected with PBS. Serum samples were collected at the times described and analyzed for neutralization (A and D) and HAI titers (B and E). A month later, these mice were challenged with a lethal dose (100 × LD50) of mouse-adapted FM1 (C and F). Naive mice (six mice) that sequentially received PBS were included as infection control (C and F). Four days following challenge, lungs of the mice were harvested and assessed for lung viral titers via plaque assay on MDCK cells, shown as plaque forming units (pfu/ml). Numbers indicate the number of mice with undetectable level of lung viral titers. Open bars represent serum titers against PR8 and filled bars against FM1. Each data point represents an individual animal. Error bars represent SEM. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.02; ***, p < 0.001. The data represent two separate experiments.